ZnO Nanoparticles-Modified Dressings to Inhibit Wound Pathogens
- PMID: 34200053
- PMCID: PMC8200248
- DOI: 10.3390/ma14113084
ZnO Nanoparticles-Modified Dressings to Inhibit Wound Pathogens
Abstract
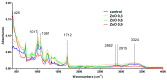
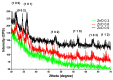
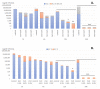
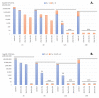
Zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles (NPs) have been investigated for various skin therapies in recent years. These NPs can improve the healing and modulate inflammation in the wounds, but the mechanisms involved in such changes are yet to be known. In this study, we have designed a facile ZnO nano-coated dressing with improved antimicrobial efficiency against typical wound pathogens involved in biofilm and chronic infections. ZnO NPs were obtained by hydrothermal method and characterized by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy. Antibacterial and antibiofilm effects were evaluated against laboratory and clinical isolates of significant Gram-negative (Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli) and Gram-positive (Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus faecalis) opportunistic pathogens, by quantitative methods. Our results have shown that the developed dressings have a high antibacterial efficiency after 6-24 h of contact when containing 0.6 and 0.9% ZnO NPs and this effect is similar against reference and clinical isolates. Moreover, biofilm development is significantly impaired for up to three days of contact, depending on the NPs load and microbial species. These results show that ZnO-coated dressings prevent biofilm development of main wound pathogens and represent efficient candidates for developing bioactive dressings to fight chronic wounds.
Keywords: ZnO nano-coatings; antimicrobial nanoparticles; biofilm control; chronic wounds; opportunistic pathogens.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

