Studies on the Catalytic Properties of Crude Freeze-Dried Preparations of Yarrowia lipolytica Extracellular Lipases for Geranyl Ester Derivative Synthesis
- PMID: 34200103
- PMCID: PMC8228730
- DOI: 10.3390/biom11060839
Studies on the Catalytic Properties of Crude Freeze-Dried Preparations of Yarrowia lipolytica Extracellular Lipases for Geranyl Ester Derivative Synthesis
Abstract
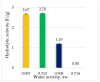
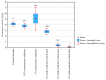
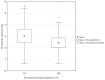
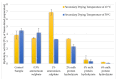
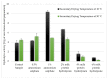
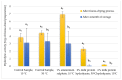
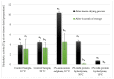
The study aimed to evaluate the impact of selected factors of the freeze-drying process on the hydrolytic and synthetic activity of the extracellular lipases of Y. lipolytica KKP 379 and to attempt the use of the crude enzyme preparation as a biocatalyst in the synthesis of geranyl 4-hydroxyphenylpropanoate. Antioxidant and antibacterial properties of the geranyl ester derivative were also investigated in order to evaluate their usefulness as a novel food additive. The studies confirmed that freeze-drying was an effective method of dehydrating yeast supernatant and allowed for obtaining lyophilizates with low water activity from 0.055 to 0.160. The type and concentration of the additive (2-6% whey protein hydrolyzate, 0.5% and 1% ammonium sulphate) had a significant effect on the hydrolytic activity of enzyme preparations, while the selected variants of drying temperature during the freeze-drying process were not significant (10 °C and 50 °C). Low yield of geranyl 4-hydroxyphenylopropionate was shown when the lyophilized supernatant was used (5.3%), but the yield of ester synthesis increased when the freeze-dried Y. lipolytica yeast biomass was applied (47.9%). The study confirmed the antioxidant properties of the synthesized ester by the DPPH• and CUPRAC methods, as well as higher antibacterial activity against tested bacteria than its precursor with 0.125 mM MIC (minimal inhibitory concentration) against L. monocytogenes.
Keywords: Yarrowia lipolytica; antibacterial; antioxidant; biocatalyst; cryoprotectant; esterification; freeze-drying; lipase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
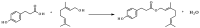
Similar articles
-
Effect of additives on freeze-drying and storage of Yarrowia lipolytica lipase.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2012 Nov;168(5):1101-7. doi: 10.1007/s12010-012-9844-z. Epub 2012 Aug 30. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22932849
-
Application of freeze-dried Yarrowia lipolytica biomass in the synthesis of lipophilic antioxidants.Biotechnol Lett. 2021 Mar;43(3):601-612. doi: 10.1007/s10529-020-03033-6. Epub 2020 Oct 26. Biotechnol Lett. 2021. PMID: 33104936 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and Application of Yarrowia lipolytica Lipase Obtained by Solid-State Fermentation in the Synthesis of Different Esters Used in the Food Industry.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2019 Nov;189(3):933-959. doi: 10.1007/s12010-019-03047-5. Epub 2019 Jun 1. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31152353
-
Yarrowia lipolytica: a beneficious yeast in biotechnology as a rare opportunistic fungal pathogen: a minireview.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018 Dec 21;35(1):10. doi: 10.1007/s11274-018-2583-8. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 30578432 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The lipases from Yarrowia lipolytica: genetics, production, regulation, biochemical characterization and biotechnological applications.Biotechnol Adv. 2011 Nov-Dec;29(6):632-44. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2011.04.005. Epub 2011 Apr 28. Biotechnol Adv. 2011. PMID: 21550394 Review.
Cited by
-
Production of cellulases by Xylaria sp. and Nemania sp. using lignocellulose substrates for bioethanol production from maize cobs.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 30;10(17):e36802. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36802. eCollection 2024 Sep 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39296107 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hasan F., Shah A.A., Hameed A. Industrial applications of microbial lipases. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2006;39:235–251. doi: 10.1016/j.enzmictec.2005.10.016. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

