Pharmacological Activities of Aminophenoxazinones
- PMID: 34200139
- PMCID: PMC8201375
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26113453
Pharmacological Activities of Aminophenoxazinones
Abstract
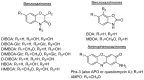
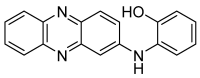
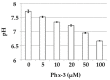
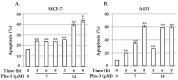
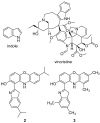
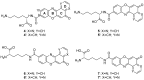
Aminophenoxazinones are degradation products resulting from the metabolism of different plant species, which comprise a family of natural products well known for their pharmacological activities. This review provides an overview of the pharmacological properties and applications proved by these compounds and their structural derivatives during 2000-2021. The bibliography was selected according to our purpose from the references obtained in a SciFinder database search for the Phx-3 structure (the base molecule of the aminophenoxazinones). Compounds Phx-1 and Phx-3 are among the most studied, especially as anticancer drugs for the treatment of gastric and colon cancer, glioblastoma and melanoma, among others types of relevant cancers. The main information available in the literature about their mechanisms is also described. Similarly, antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral and antiparasitic activities are presented, including species related directly or indirectly to significant diseases. Therefore, we present diverse compounds based on aminophenoxazinones with high potential as drugs, considering their levels of activity and few adverse effects.
Keywords: Phx-3; aminophenoxazinone; antibacterial; antifungal; cancer; cytotoxicity; drug; in vitro; in vivo; virus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


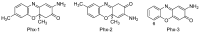

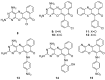


References
-
- Sánchez-Moreiras A.M., Coba de la Peña T., Martínez A., González L., Pellisier F., Reigosa M.J. Mode of action of the hydroxamic acid BOA and other related compounds. Allelopathy. 2004:239–252.
-
- Jensen B.M., Adhikari K.B., Schnoor H.J., Juel-Berg N., Fomsgaard I.S., Poulsen L.K. Quantitative analysis of absorption, metabolism, and excretion of benzoxazinoids in humans after the consumption of high- and low-benzoxazinoid diets with similar contents of cereal dietary fibres: A crossover study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017;56:387–397. doi: 10.1007/s00394-015-1088-6. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

