Adversarial Attack and Defence through Adversarial Training and Feature Fusion for Diabetic Retinopathy Recognition
- PMID: 34200216
- PMCID: PMC8201392
- DOI: 10.3390/s21113922
Adversarial Attack and Defence through Adversarial Training and Feature Fusion for Diabetic Retinopathy Recognition
Abstract
Due to the rapid growth in artificial intelligence (AI) and deep learning (DL) approaches, the security and robustness of the deployed algorithms need to be guaranteed. The security susceptibility of the DL algorithms to adversarial examples has been widely acknowledged. The artificially created examples will lead to different instances negatively identified by the DL models that are humanly considered benign. Practical application in actual physical scenarios with adversarial threats shows their features. Thus, adversarial attacks and defense, including machine learning and its reliability, have drawn growing interest and, in recent years, has been a hot topic of research. We introduce a framework that provides a defensive model against the adversarial speckle-noise attack, the adversarial training, and a feature fusion strategy, which preserves the classification with correct labelling. We evaluate and analyze the adversarial attacks and defenses on the retinal fundus images for the Diabetic Retinopathy recognition problem, which is considered a state-of-the-art endeavor. Results obtained on the retinal fundus images, which are prone to adversarial attacks, are 99% accurate and prove that the proposed defensive model is robust.
Keywords: adversarial attack; adversarial training; deep learning; diabetic retinopathy; feature fusion; speckle-noise attack.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
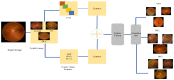
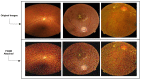
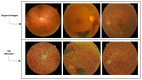
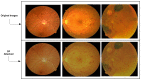
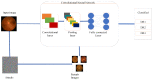
References
-
- Albahli S., Rauf H.T., Arif M., Nafis M.T., Algosaibi A. Identification of Thoracic Diseases by Exploiting Deep Neural Networks. Neural Netw. 2021;5:6.
-
- Abdulsahib A.A., Mahmoud M.A., Mohammed M.A., Rasheed H.H., Mostafa S.A., Maashi M.S. Comprehensive review of retinal blood vessel segmentation and classification techniques: Intelligent solutions for green computing in medical images, current challenges, open issues, and knowledge gaps in fundus medical images. Netw. Model. Anal. Health Inform. Bioinform. 2021;10:1–32.
-
- Canedo D., Neves A.J.R. Facial Expression Recognition Using Computer Vision: A Systematic Review. Appl. Sci. 2019;9:4678. doi: 10.3390/app9214678. - DOI
-
- Kour N., Sunanda, Arora S. Computer-vision based diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease via gait: A survey. IEEE Access. 2019;7:156620–156645. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2949744. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

