NKG2D Natural Killer Cell Receptor-A Short Description and Potential Clinical Applications
- PMID: 34200375
- PMCID: PMC8229527
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10061420
NKG2D Natural Killer Cell Receptor-A Short Description and Potential Clinical Applications
Abstract
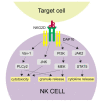
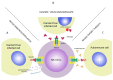
Natural Killer (NK) cells are natural cytotoxic, effector cells of the innate immune system. They can recognize transformed or infected cells. NK cells are armed with a set of activating and inhibitory receptors which are able to bind to their ligands on target cells. The right balance between expression and activation of those receptors is fundamental for the proper functionality of NK cells. One of the best known activating receptors is NKG2D, a member of the CD94/NKG2 family. Due to a specific NKG2D binding with its eight different ligands, which are overexpressed in transformed, infected and stressed cells, NK cells are able to recognize and attack their targets. The NKG2D receptor has an enormous significance in various, autoimmune diseases, viral and bacterial infections as well as for transplantation outcomes and complications. This review focuses on the NKG2D receptor, the mechanism of its action, clinical relevance of its gene polymorphisms and a potential application in various clinical settings.
Keywords: NK cells; NKG2D ligands; NKG2D receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Stewart C.A., Vivier E., Colonna M. Strategies of Natural Killer Cell Recognition and Signaling. In: Vivier E., Colonna M., editors. Immunobiology of Natural Killer Cell Receptors. Volume 298. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2006. pp. 1–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

