Current Knowledge on Beetroot Bioactive Compounds: Role of Nitrate and Betalains in Health and Disease
- PMID: 34200431
- PMCID: PMC8229785
- DOI: 10.3390/foods10061314
Current Knowledge on Beetroot Bioactive Compounds: Role of Nitrate and Betalains in Health and Disease
Abstract
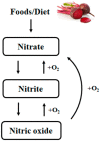
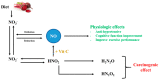
An increase in the prevalence of noncommunicable chronic diseases has been occurring in recent decades. Among the deaths resulting from these conditions, cardiovascular diseases (CVD) stand out as the main contributors. In this regard, dietary patterns featuring a high content of vegetables and fruits, such as the Mediterranean and the DASH diets, are considered beneficial, and thus have been extensively studied. This has resulted in growing interest in vegetable-derived ingredients and food-supplements that may have potential therapeutic properties. Among these supplements, beetroot juice, which is obtained from the root vegetable Beta vulgaris, has gained much attention. Although a significant part of the interest in beetroot juice is due to its nitrate (NO3-) content, which has demonstrated bioactivity in the cardiovascular system, other ingredients with potential beneficial properties such as polyphenols, pigments and organic acids are also present. In this context, the aim of this review article is to analyze the current knowledge regarding the benefits related to the consumption of beetroot and derived food-supplements. Therefore, this article focuses on nitrate and betalains, which are considered to be the major bioactive compounds present in beetroot, and thus in the derived dietary supplements.
Keywords: beetroot; betalains; dietary supplement; nitrate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Papadaki A., Martínez-González M.A., Alonso-Gómez A., Rekondo J., Salas-Salvadó J., Corella D., Ros E., Fitó M., Estruch R., Lapetra J., et al. Mediterranean diet and risk of heart failure: Results from the PREDIMED randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2017;19:1179–1185. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.750. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

