Lyme Neuroborreliosis in Children
- PMID: 34200467
- PMCID: PMC8226969
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci11060758
Lyme Neuroborreliosis in Children
Abstract
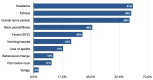
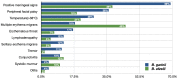
Lyme neuroborreliosis (LNB) is an infectious disease, developing after a tick bite and the dissemination of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato spirochetes reach the nervous system. The infection occurs in children and adults but with different clinical courses. Adults complain of radicular pain and paresis, while among the pediatric population, the most common manifestations of LNB are facial nerve palsy and/or subacute meningitis. Moreover, atypical symptoms, such as fatigue, loss of appetite, or mood changes, may also occur. The awareness of the various clinical features existence presented by children with LNB suspicion remains to be of the greatest importance to diagnose and manage the disease.
Keywords: children; diagnosis; facial nerve palsy; lyme borreliosis; meningitis; neuroborreliosis; neurological manifestations; treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources