Rare-Earth Oxides as Alternative High-Energy Photon Protective Fillers in HDPE Composites: Theoretical Aspects
- PMID: 34200711
- PMCID: PMC8230413
- DOI: 10.3390/polym13121930
Rare-Earth Oxides as Alternative High-Energy Photon Protective Fillers in HDPE Composites: Theoretical Aspects
Abstract
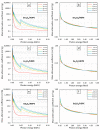
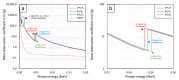
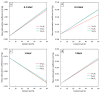
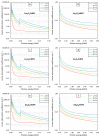
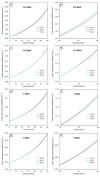
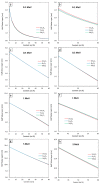
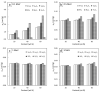
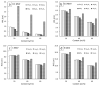
This work theoretically determined the high-energy photon shielding properties of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) composites containing rare-earth oxides, namely samarium oxide (Sm2O3), europium oxide (Eu2O3), and gadolinium oxide (Gd2O3), for potential use as lead-free X-ray-shielding and gamma-shielding materials using the XCOM software package. The considered properties were the mass attenuation coefficient (µm), linear attenuation coefficient (µ), half value layer (HVL), and lead equivalence (Pbeq) that were investigated at varying photon energies (0.001-5 MeV) and filler contents (0-60 wt.%). The results were in good agreement (less than 2% differences) with other available programs (Phy-X/PSD) and Monte Carlo particle transport simulation code, namely PHITS, which showed that the overall high-energy photon shielding abilities of the composites considerably increased with increasing rare-earth oxide contents but reduced with increasing photon energies. In particular, the Gd2O3/HDPE composites had the highest µm values at photon energies of 0.1, 0.5, and 5 MeV, due to having the highest atomic number (Z). Furthermore, the Pbeq determination of the composites within the X-ray energy ranges indicated that the 10 mm thick samples with filler contents of 40 wt.% and 50 wt.% had Pbeq values greater than the minimum requirements for shielding materials used in general diagnostic X-ray rooms and computerized tomography rooms, which required Pbeq values of at least 1.0 and 1.5 mmPb, respectively. In addition, the comparisons of µm, µ, and HVL among the rare-earth oxide/HDPE composites investigated in this work and other lead-free X-ray shielding composites revealed that the materials developed in this work exhibited comparable X-ray shielding properties in comparison with that of the latter, implying great potential to be used as effective X-ray shielding materials in actual applications.
Keywords: Eu2O3; Gd2O3; HDPE; Sm2O3; X-ray; XCOM; gamma; photon; shielding.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; the writing of the manuscript; or the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparative X-ray Shielding Properties of Single-Layered and Multi-Layered Bi2O3/NR Composites: Simulation and Numerical Studies.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Apr 27;14(9):1788. doi: 10.3390/polym14091788. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35566961 Free PMC article.
-
High-Energy Photon Attenuation Properties of Lead-Free and Self-Healing Poly (Vinyl Alcohol) (PVA) Hydrogels: Numerical Determination and Simulation.Gels. 2022 Mar 22;8(4):197. doi: 10.3390/gels8040197. Gels. 2022. PMID: 35448098 Free PMC article.
-
Theoretical Determination of High-Energy Photon Attenuation and Recommended Protective Filler Contents for Flexible and Enhanced Dimensionally Stable Wood/NR and NR Composites.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Mar 11;13(6):869. doi: 10.3390/polym13060869. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33799832 Free PMC article.
-
Shielding characteristics of nanocomposites for protection against X- and gamma rays in medical applications: effect of particle size, photon energy and nano-particle concentration.Radiat Environ Biophys. 2020 Nov;59(4):583-600. doi: 10.1007/s00411-020-00865-8. Epub 2020 Aug 11. Radiat Environ Biophys. 2020. PMID: 32780196 Review.
-
Development of Lead-Free Materials for Radiation Shielding in Medical Settings: A Review.J Biomed Phys Eng. 2024 Jun 1;14(3):229-244. doi: 10.31661/jbpe.v0i0.2404-1742. eCollection 2024 Jun. J Biomed Phys Eng. 2024. PMID: 39027711 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Comparative Study on X-ray Shielding and Mechanical Properties of Natural Rubber Latex Nanocomposites Containing Bi2O3 or BaSO4: Experimental and Numerical Determination.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Sep 2;14(17):3654. doi: 10.3390/polym14173654. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36080729 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative X-ray Shielding Properties of Single-Layered and Multi-Layered Bi2O3/NR Composites: Simulation and Numerical Studies.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Apr 27;14(9):1788. doi: 10.3390/polym14091788. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35566961 Free PMC article.
-
High-Energy Photon Attenuation Properties of Lead-Free and Self-Healing Poly (Vinyl Alcohol) (PVA) Hydrogels: Numerical Determination and Simulation.Gels. 2022 Mar 22;8(4):197. doi: 10.3390/gels8040197. Gels. 2022. PMID: 35448098 Free PMC article.
-
Highly Efficient and Eco-Friendly Thermal-Neutron-Shielding Materials Based on Recycled High-Density Polyethylene and Gadolinium Oxide Composites.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Apr 18;16(8):1139. doi: 10.3390/polym16081139. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38675059 Free PMC article.
-
Progress in Flexible and Wearable Lead-Free Polymer Composites for Radiation Protection.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Nov 25;16(23):3274. doi: 10.3390/polym16233274. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39684019 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Matsuyama S., Maeshima K., Shimura M. Development of X-ray imaging of intracellular elements and structure. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2020;35:1279–1294. doi: 10.1039/D0JA00128G. - DOI
-
- Sitz A., Hoevels M., Hellerbach A., Gierich A., Luyken K., Dembek T.A., Klehr M., Wirths J., Visser-Vandewalle V., Treuer H. Determining the orientation angle of directional leads for deep brain stimulation using computed tomography and digital x-ray imaging: A phantom study. Med. Phys. 2017;44:4463–4473. doi: 10.1002/mp.12424. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ulukapi K., Ozmen S.F. Study of the effect of irradiation (60Co) on M1 plants of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) cultivars and determined [sic] of proper doses for mutation breeding. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2018;11:157–161. doi: 10.1016/j.jrras.2017.12.004. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

