Comparative Genomics of Eight Fusarium graminearum Strains with Contrasting Aggressiveness Reveals an Expanded Open Pangenome and Extended Effector Content Signatures
- PMID: 34200775
- PMCID: PMC8230406
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22126257
Comparative Genomics of Eight Fusarium graminearum Strains with Contrasting Aggressiveness Reveals an Expanded Open Pangenome and Extended Effector Content Signatures
Abstract
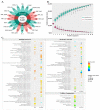
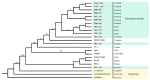
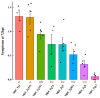
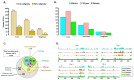
Fusarium graminearum, the primary cause of Fusarium head blight (FHB) in small-grain cereals, demonstrates remarkably variable levels of aggressiveness in its host, producing different infection dynamics and contrasted symptom severity. While the secreted proteins, including effectors, are thought to be one of the essential components of aggressiveness, our knowledge of the intra-species genomic diversity of F. graminearum is still limited. In this work, we sequenced eight European F. graminearum strains of contrasting aggressiveness to characterize their respective genome structure, their gene content and to delineate their specificities. By combining the available sequences of 12 other F. graminearum strains, we outlined a reference pangenome that expands the repertoire of the known genes in the reference PH-1 genome by 32%, including nearly 21,000 non-redundant sequences and gathering a common base of 9250 conserved core-genes. More than 1000 genes with high non-synonymous mutation rates may be under diverse selection, especially regarding the trichothecene biosynthesis gene cluster. About 900 secreted protein clusters (SPCs) have been described. Mostly localized in the fast sub-genome of F. graminearum supposed to evolve rapidly to promote adaptation and rapid responses to the host's infection, these SPCs gather a range of putative proteinaceous effectors systematically found in the core secretome, with the chloroplast and the plant nucleus as the main predicted targets in the host cell. This work describes new knowledge on the intra-species diversity in F. graminearum and emphasizes putative determinants of aggressiveness, providing a wealth of new candidate genes potentially involved in the Fusarium head blight disease.
Keywords: Fusarium graminearum; Fusarium head blight; aggressiveness; intra-species genomic diversity; pangenome; proteinaceous effectors; secreted protein clusters.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Desjardins A.E. Fusarium Mycotoxins: Chemistry, Genetics, and Biology. APS Press; St. Paul, MN, USA: 2006.
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

