Systemic Antibiotic Prophylaxis to Reduce Early Implant Failure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 34200841
- PMCID: PMC8230529
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics10060698
Systemic Antibiotic Prophylaxis to Reduce Early Implant Failure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Systemic antibiotics are routinely prescribed in implant procedures, but the lack of consensus causes large differences between clinicians regarding antibiotic prophylaxis regimens. The objectives of this systematic review are to assess the need to prescribe antibiotics to prevent early implant failure and find the most appropriate antibiotic prophylaxis regimen. The electronic search was conducted in PubMed/MEDLINE, Scielo and Cochrane Central Trials Database for randomized clinical trials of at least 3 months of follow-up. Eleven studies were included in the qualitative analysis. Antibiotics were found to statistically significantly reduce early implant failures (RR = 0.30, 95% CI: 0.19-0.47, p < 0.00001; heterogeneity I2 = 0%, p = 0.54). No differences were seen between preoperative or both pre- and postoperative antibiotic regimens (RR = 0.57, 95% CI: 0.21-1.55, p = 0.27; heterogeneity I2 = 0%, p = 0.37). A single preoperative antibiotic prophylaxis dose was found to be enough to significantly reduce early implant failures compared to no antibiotic (RR = 0.34, 95% CI: 0.21-0.53, p < 0.00001; heterogeneity I2 = 0%, p = 0.61). In conclusion, in healthy patients a single antibiotic prophylaxis dose is indicated to prevent early implant failure.
Keywords: antibiotics; dental implants; early implant failure; meta-analysis; systematic review; systemic antibiotic prophylaxis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
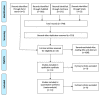



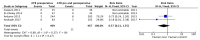
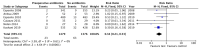
References
-
- Van Steenberghe D., Jacobs R., Desnyder M., Maffei G., Quirynen M. The relative impact of local and endogenous patient-related factors on implant failure up to the abutment stage: Early implant failure. Clin. Oral. Implants Res. 2002;13:617–622. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0501.2002.130607.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Troiano G., Lo Russo L., Canullo L., Ciavarella D., Lo Muzio L., Laino L. Early and late implant failure of submerged versus non-submerged implant healing: A systematic review, meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018;45:613–623. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12890. - DOI - PubMed

