Primary Cilium Is Involved in Stem Cell Differentiation and Renewal through the Regulation of Multiple Signaling Pathways
- PMID: 34201019
- PMCID: PMC8226522
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10061428
Primary Cilium Is Involved in Stem Cell Differentiation and Renewal through the Regulation of Multiple Signaling Pathways
Abstract
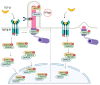
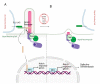
Signaling networks guide stem cells during their lineage specification and terminal differentiation. Primary cilium, an antenna-like protrusion, directly or indirectly plays a significant role in this guidance. All stem cells characterized so far have primary cilia. They serve as entry- or check-points for various signaling events by controlling the signal transduction and stability. Thus, defects in the primary cilia formation or dynamics cause developmental and health problems, including but not limited to obesity, cardiovascular and renal anomalies, hearing and vision loss, and even cancers. In this review, we focus on the recent findings of how primary cilium controls various signaling pathways during stem cell differentiation and identify potential gaps in the field for future research.
Keywords: Notch; TGF; Wnt; cancer stem cells; differentiation; mTOR; primary cilia; signaling; stem cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

