Glutathione Deficiency during Early Postnatal Development Causes Schizophrenia-Like Symptoms and a Reduction in BDNF Levels in the Cortex and Hippocampus of Adult Sprague-Dawley Rats
- PMID: 34201038
- PMCID: PMC8229148
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22126171
Glutathione Deficiency during Early Postnatal Development Causes Schizophrenia-Like Symptoms and a Reduction in BDNF Levels in the Cortex and Hippocampus of Adult Sprague-Dawley Rats
Abstract
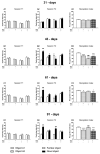
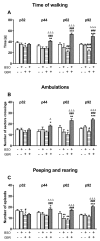
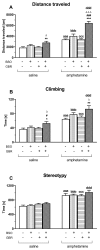
Growing body of evidence points to dysregulation of redox status in the brain as an important factor in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia. The aim of our study was to evaluate the effects of l-buthionine-(S,R)-sulfoximine (BSO), a glutathione (GSH) synthesis inhibitor, and 1-[2-Bis(4-fluorophenyl)methoxy]ethyl]-4-(3-phenylpropyl)piperazine dihydrochloride (GBR 12909), a dopamine reuptake inhibitor, given alone or in combination, to Sprague-Dawley pups during early postnatal development (p5-p16), on the time course of the onset of schizophrenia-like behaviors, and on the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) mRNA and its protein in the prefrontal cortex (PFC) and hippocampus (HIP) during adulthood. BSO administered alone decreased the levels of BDNF mRNA and its protein both in the PFC and HIP. Treatment with the combination of BSO + GBR 12909 also decreased BDNF mRNA and its protein in the PFC, but in the HIP, only the level of BDNF protein was decreased. Schizophrenia-like behaviors in rats were assessed at three time points of adolescence (p30, p42-p44, p60-p62) and in early adulthood (p90-p92) using the social interaction test, novel object recognition test, and open field test. Social and cognitive deficits first appeared in the middle adolescence stage and continued to occur into adulthood, both in rats treated with BSO alone or with the BSO + GBR 12909 combination. Behavior corresponding to positive symptoms in humans occurred in the middle adolescence period, only in rats treated with BSO + GBR 12909. Only in the latter group, amphetamine exacerbated the existing positive symptoms in adulthood. Our data show that rats receiving the BSO + GBR 12909 combination in the early postnatal life reproduced virtually all symptoms observed in patients with schizophrenia and, therefore, can be considered a valuable neurodevelopmental model of this disease.
Keywords: effect of amphetamine; levels of BDNF mRNA and its protein; neurodevelopmental model of schizophrenia; schizophrenia-like symptoms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Impact of repeated co-treatment with escitalopram and aripiprazole on the schizophrenia-like behaviors and BDNF mRNA expression in the adult Sprague-Dawley rats exposed to glutathione deficit during early postnatal development of the brain.Pharmacol Rep. 2021 Dec;73(6):1712-1723. doi: 10.1007/s43440-021-00318-z. Epub 2021 Aug 16. Pharmacol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34398437 Free PMC article.
-
Repeated co-treatment with mirtazapine and aripiprazole reversed the schizophrenia-like behaviors and increased the brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA expression in the adult Sprague-Dawley rats exposed to glutathione deficit during early postnatal brain development.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2021 Oct;72(5). doi: 10.26402/jpp.2021.5.05. Epub 2022 Feb 12. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 35158332
-
Glutathione Deficiency and Alterations in the Sulfur Amino Acid Homeostasis during Early Postnatal Development as Potential Triggering Factors for Schizophrenia-Like Behavior in Adult Rats.Molecules. 2019 Nov 22;24(23):4253. doi: 10.3390/molecules24234253. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31766654 Free PMC article.
-
Neurobiology of schizophrenia onset.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2014;16:267-95. doi: 10.1007/7854_2013_243. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 23975845 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Genesis of Schizophrenia: An Origin Story.Am J Psychiatry. 2024 Jun 1;181(6):482-492. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.20240305. Am J Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38822584 Review.
Cited by
-
Iron administered in the neonatal period changed memory, brain monoamine levels, and BDNF mRNA expression in adult Sprague-Dawley rats.Pharmacol Rep. 2024 Oct;76(5):1044-1054. doi: 10.1007/s43440-024-00626-0. Epub 2024 Jul 16. Pharmacol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39012420 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Glutathione Deficit During Early Postnatal Brain Development on the Prepulse Inhibition and Monoamine Levels in Brain Structures of Adult Sprague-Dawley Rats.Neurotox Res. 2022 Jun;40(3):733-750. doi: 10.1007/s12640-022-00496-5. Epub 2022 Apr 7. Neurotox Res. 2022. PMID: 35386024
-
Is There a Glutathione Centered Redox Dysregulation Subtype of Schizophrenia?Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Oct 27;10(11):1703. doi: 10.3390/antiox10111703. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34829575 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Schizophrenia Synaptic Pathology and Antipsychotic Treatment in the Framework of Oxidative and Mitochondrial Dysfunction: Translational Highlights for the Clinics and Treatment.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Apr 21;12(4):975. doi: 10.3390/antiox12040975. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37107350 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effect of phencyclidine-mediated blockade of NMDA receptors in the early postnatal period on glutathione and sulfur amino acid levels in the rat brain as a potential causative factor of schizophrenia-like behavior in adulthood.Pharmacol Rep. 2024 Aug;76(4):863-877. doi: 10.1007/s43440-024-00607-3. Epub 2024 Jun 21. Pharmacol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38904712 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

