MoGLN2 Is Important for Vegetative Growth, Conidiogenesis, Maintenance of Cell Wall Integrity and Pathogenesis of Magnaporthe oryzae
- PMID: 34201222
- PMCID: PMC8229676
- DOI: 10.3390/jof7060463
MoGLN2 Is Important for Vegetative Growth, Conidiogenesis, Maintenance of Cell Wall Integrity and Pathogenesis of Magnaporthe oryzae
Abstract
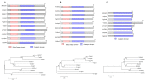
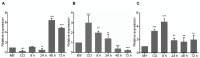
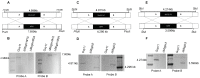
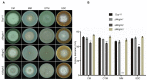
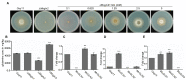
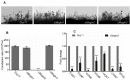
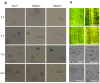
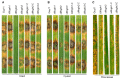
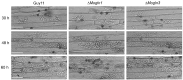
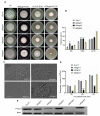
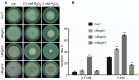
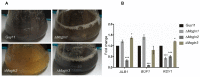
Glutamine is a non-essential amino acid that acts as a principal source of nitrogen and nucleic acid biosynthesis in living organisms. In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, glutamine synthetase catalyzes the synthesis of glutamine. To determine the role of glutamine synthetase in the development and pathogenicity of plant fungal pathogens, we used S. cerevisiae Gln1 amino acid sequence to identify its orthologs in Magnaporthe oryzae and named them MoGln1, MoGln2, and MoGln3. Deletion of MoGLN1 and MoGLN3 showed that they are not involved in the development and pathogenesis of M. oryzae. Conversely, ΔMogln2 was reduced in vegetative growth, experienced attenuated growth on Minimal Medium (MM), and exhibited hyphal autolysis on oatmeal and straw decoction and corn media. Exogenous l-glutamine rescued the growth of ΔMogln2 on MM. The ΔMogln2 mutant failed to produce spores and was nonpathogenic on barley leaves, as it was unable to form an appressorium-like structure from its hyphal tips. Furthermore, deletion of MoGLN2 altered the fungal cell wall integrity, with the ΔMogln2 mutant being hypersensitive to H2O2. MoGln1, MoGln2, and MoGln3 are located in the cytoplasm. Taken together, our results shows that MoGLN2 is important for vegetative growth, conidiation, appressorium formation, maintenance of cell wall integrity, oxidative stress tolerance and pathogenesis of M. oryzae.
Keywords: Magnaporthe oryzae; cell wall integrity; glutamine; glutamine synthetase; pathogenicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MoCpa1-mediated arginine biosynthesis is crucial for fungal growth, conidiation, and plant infection of Magnaporthe oryzae.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Aug;105(14-15):5915-5929. doi: 10.1007/s00253-021-11437-1. Epub 2021 Jul 22. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34292355
-
De novo purine nucleotide biosynthesis mediated by MoAde4 is required for conidiation, host colonization and pathogenicity in Magnaporthe oryzae.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 Sep;106(17):5587-5602. doi: 10.1007/s00253-022-12100-z. Epub 2022 Aug 3. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35918446
-
MoGT2 Is Essential for Morphogenesis and Pathogenicity of Magnaporthe oryzae.mSphere. 2019 Sep 4;4(5):e00309-19. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00309-19. mSphere. 2019. PMID: 31484736 Free PMC article.
-
MoTup1 is required for growth, conidiogenesis and pathogenicity of Magnaporthe oryzae.Mol Plant Pathol. 2015 Oct;16(8):799-810. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12235. Epub 2015 Feb 27. Mol Plant Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25583028 Free PMC article.
-
MoGrr1, a novel F-box protein, is involved in conidiogenesis and cell wall integrity and is critical for the full virulence of Magnaporthe oryzae.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015 Oct;99(19):8075-88. doi: 10.1007/s00253-015-6820-x. Epub 2015 Jul 31. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 26227409
Cited by
-
The Devastating Rice Blast Airborne Pathogen Magnaporthe oryzae-A Review on Genes Studied with Mutant Analysis.Pathogens. 2023 Feb 26;12(3):379. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12030379. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 36986301 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AGC/AKT Protein Kinase SCH9 Is Critical to Pathogenic Development and Overwintering Survival in Magnaporthe oryzae.J Fungi (Basel). 2022 Jul 31;8(8):810. doi: 10.3390/jof8080810. J Fungi (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36012798 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Phosphatases MoPtc5, MoPtc1, and MoPtc2 Contribute to the Vegetative Growth, Stress Adaptation, and Virulence of Magnaporthe oryzae.J Fungi (Basel). 2025 Mar 18;11(3):231. doi: 10.3390/jof11030231. J Fungi (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40137268 Free PMC article.
-
MoHG1 Regulates Fungal Development and Virulence in Magnaporthe oryzae.J Fungi (Basel). 2024 Sep 21;10(9):663. doi: 10.3390/jof10090663. J Fungi (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39330422 Free PMC article.
-
Type 2C Protein Phosphatases MoPtc5 and MoPtc7 Are Crucial for Multiple Stress Tolerance, Conidiogenesis and Pathogenesis of Magnaporthe oryzae.J Fungi (Basel). 2022 Dec 20;9(1):1. doi: 10.3390/jof9010001. J Fungi (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36675822 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

