New Therapies to Correct the Cystic Fibrosis Basic Defect
- PMID: 34201249
- PMCID: PMC8227161
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22126193
New Therapies to Correct the Cystic Fibrosis Basic Defect
Abstract
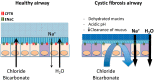
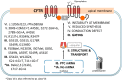
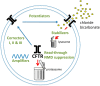
Rare diseases affect 400 million individuals worldwide and cause significant morbidity and mortality. Finding solutions for rare diseases can be very challenging for physicians and researchers. Cystic fibrosis (CF), a genetic, autosomal recessive, multisystemic, life-limiting disease does not escape this sad reality. Despite phenomenal progress in our understanding of this disease, treatment remains difficult. Until recently, therapies for CF individuals were focused on symptom management. The discovery of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene and its product, a protein present at the apical surface of epithelial cells regulating ion transport, allowed the scientific community to learn about the basic defect in CF and to study potential therapies targeting the dysfunctional protein. In the past few years, promising therapies with the goal to restore CFTR function became available and changed the lives of several CF patients. These medications, called CFTR modulators, aim to correct, potentialize, stabilize or amplify CFTR function. Furthermore, research is ongoing to develop other targeted therapies that could be more efficient and benefit a larger proportion of the CF community. The purpose of this review is to summarize our current knowledge of CF genetics and therapies restoring CFTR function, particularly CFTR modulators and gene therapy.
Keywords: CFTR; CFTR modulators; cystic fibrosis; gene therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
C.B. has no conflict of interest to declare. A.M.C. has received honoraria from Vertex Pharmaceuticals (Canada) Incorporated for development of the educational module CF Annual year in review, which is outside of the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- Cftr2 Database. [(accessed on 20 May 2021)]; Available online: https://cftr2.org/
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

