Multidrug Resistance Like Protein 1 Activity in Malpighian Tubules Regulates Lipid Homeostasis in Drosophila
- PMID: 34201304
- PMCID: PMC8229909
- DOI: 10.3390/membranes11060432
Multidrug Resistance Like Protein 1 Activity in Malpighian Tubules Regulates Lipid Homeostasis in Drosophila
Abstract
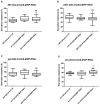
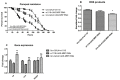
Multidrug resistance proteins (MRPs), members of the ATP-binding cassette transporter (ABC transporter) family, are pivotal for transporting endo- and xenobiotics, which confer resistance to anticancer agents and contribute to the clearance of oxidative products. However, their function in many biological processes is still unclear. We investigated the role of an evolutionarily conserved MRP in metabolic homeostasis by knocking down the expression of Drosophila multidrug-resistance like protein 1 (MRP) in several tissues involved in regulating metabolism, including the gut, fat body, and Malpighian tubules. Interestingly, only suppression of MRP in the Malpighian tubules, the functional equivalent to the human kidney, was sufficient to cause abnormal lipid accumulation and disrupt feeding behavior. Furthermore, reduced Malpighian tubule MRP expression resulted in increased Hr96 (homolog of human pregnane X receptor) expression. Hr96 is known to play a role in detoxification and lipid metabolism processes. Reduced expression of MRP in the Malpighian tubules also conveyed resistance to oxidative stress, as well as reduced normal levels of reactive oxygen species in adult flies. This study reveals that an evolutionarily conserved MRP is required in Drosophila Malpighian tubules for proper metabolic homeostasis.
Keywords: ABCC1; kidney; lipid metabolism; oxidative stress; xenobiotic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Target organ specific activity of drosophila MRP (ABCC1) moderates developmental toxicity of methylmercury.Toxicol Sci. 2014 Aug 1;140(2):425-35. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfu095. Epub 2014 May 25. Toxicol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24863968 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic knockdown of a single organic anion transporter alters the expression of functionally related genes in Malpighian tubules of Drosophila melanogaster.J Exp Biol. 2012 Aug 1;215(Pt 15):2601-10. doi: 10.1242/jeb.071100. J Exp Biol. 2012. PMID: 22786636
-
Dibutyl Phthalate Exposure Disrupts Evolutionarily Conserved Insulin and Glucagon-Like Signaling in Drosophila Males.Endocrinology. 2016 Jun;157(6):2309-21. doi: 10.1210/en.2015-2006. Epub 2016 Apr 21. Endocrinology. 2016. PMID: 27100621
-
Substrates and inhibitors of human multidrug resistance associated proteins and the implications in drug development.Curr Med Chem. 2008;15(20):1981-2039. doi: 10.2174/092986708785132870. Curr Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 18691054 Review.
-
The MRP family and anticancer drug metabolism.Curr Drug Metab. 2001 Dec;2(4):367-77. doi: 10.2174/1389200013338289. Curr Drug Metab. 2001. PMID: 11766988 Review.
Cited by
-
Drug resistance mechanisms in cancers: Execution of pro-survival strategies.J Biomed Res. 2024 Feb 28;38(2):95-121. doi: 10.7555/JBR.37.20230248. J Biomed Res. 2024. PMID: 38413011 Free PMC article.
-
Biological Membranes as Targets for Natural and Synthetic Compounds.Membranes (Basel). 2022 Nov 22;12(12):1172. doi: 10.3390/membranes12121172. Membranes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36557079 Free PMC article.
-
ame-miR-34 Modulates the Larval Body Weight and Immune Response of Apis mellifera Workers to Ascosphara apis Invasion.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 7;24(2):1214. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021214. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674732 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

