Effects of Inclusion of Schizochytrium spp. and Forage-to-Concentrate Ratios on Goats' Milk Quality and Oxidative Status
- PMID: 34201334
- PMCID: PMC8228103
- DOI: 10.3390/foods10061322
Effects of Inclusion of Schizochytrium spp. and Forage-to-Concentrate Ratios on Goats' Milk Quality and Oxidative Status
Abstract
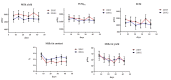
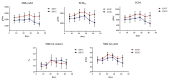
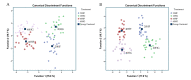
Although the dietary inclusion level of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) and the forage: concentrate (F:C) ratio affect milk quality, their interaction has not been broadly studied. To address such gaps and limitations a two-phase trial using twenty-two dairy goats was carried out. During the first phase, both groups (20 HF n = 11; high forage and 20 HG n = 11; high grain) were supplemented with 20 g Schizochytrium spp./goat/day. The 20 HF group consumed a diet with F:C ratio 60:40 and the 20 HG-diet consisted of F:C = 40:60. In the second phase, the supplementation level of Schizochytrium spp. was increased to 40 g/day/goat while the F:C ratio between the two groups were remained identical (40 HF n = 11; high forage and 40 HG n = 11; high grain). Neither the Schizochytrium spp. supplementation levels (20 vs. 40) nor the F:C ratio (60:40 vs. 40:60) affected milk performance. The high microalgae level (40 g) in combination with high grain diet (40 HG) modified the proportions of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), docosapentaenoic acid (DPA), and conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) and the ω3/ω6 ratio in milk, to a beneficial manner according to human health recommendation guidelines. However, the highest inclusion level of Schizochytrium spp. (40 g) and foremost in combination with the high grain diets (40 HG) induced an oxidative response as observed by the increased protein carbonyls (CP) and malondialdehyde (MDA) levels in milk and blood plasma indicating severe limitations for a long-term, on-farm application. In conclusion, the supplementation with 20 g Schizochytrium spp. and high forage diet (60:40) appears to be an ideal formula to enrich dairy products with essential biomolecules for human health without adversely affect milk oxidative stability.
Keywords: DHA; MDA; TAC; antioxidant; fatty acid; forage; grains; microalgae; rumen; starch.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Toral P.G., Hervás G., Gómez-Cortés P., Frutos P., Juárez M., de la Fuente M.A. Milk fatty acid profile and dairy sheep performance in response to diet supplementation with sunflower oil plus incremental levels of marine algae. J. Dairy Sci. 2010;93:1655–1667. doi: 10.3168/jds.2009-2769. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

