CBP/p300: Critical Co-Activators for Nuclear Steroid Hormone Receptors and Emerging Therapeutic Targets in Prostate and Breast Cancers
- PMID: 34201346
- PMCID: PMC8229436
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13122872
CBP/p300: Critical Co-Activators for Nuclear Steroid Hormone Receptors and Emerging Therapeutic Targets in Prostate and Breast Cancers
Abstract
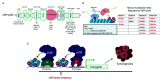
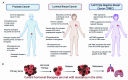
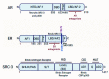
The CREB-binding protein (CBP) and p300 are two paralogous lysine acetyltransferases (KATs) that were discovered in the 1980s-1990s. Since their discovery, CBP/p300 have emerged as important regulatory proteins due to their ability to acetylate histone and non-histone proteins to modulate transcription. Work in the last 20 years has firmly established CBP/p300 as critical regulators for nuclear hormone signaling pathways, which drive tumor growth in several cancer types. Indeed, CBP/p300 are critical co-activators for the androgen receptor (AR) and estrogen receptor (ER) signaling in prostate and breast cancer, respectively. The AR and ER are stimulated by sex hormones and function as transcription factors to regulate genes involved in cell cycle progression, metabolism, and other cellular functions that contribute to oncogenesis. Recent structural studies of the AR/p300 and ER/p300 complexes have provided critical insights into the mechanism by which p300 interacts with and activates AR- and ER-mediated transcription. Breast and prostate cancer rank the first and forth respectively in cancer diagnoses worldwide and effective treatments are urgently needed. Recent efforts have identified specific and potent CBP/p300 inhibitors that target the acetyltransferase activity and the acetytllysine-binding bromodomain (BD) of CBP/p300. These compounds inhibit AR signaling and tumor growth in prostate cancer. CBP/p300 inhibitors may also be applicable for treating breast and other hormone-dependent cancers. Here we provide an in-depth account of the critical roles of CBP/p300 in regulating the AR and ER signaling pathways and discuss the potential of CBP/p300 inhibitors for treating prostate and breast cancer.
Keywords: CBP/p300; acetyltransferase; breast cancer; bromodomain; cancer epigenetics; histone acetylation; prostate cancer; transcription co-activator.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures

References
-
- Eckner R., Ewen M.E., Newsome D., Gerdes M., DeCaprio J.A., Lawrence J.B., Livingston D.M. Molecular cloning and functional analysis of the adenovirus E1A-associated 300-kD protein (p300) reveals a protein with properties of a transcriptional adaptor. Genes Dev. 1994;8:869–884. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.8.869. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

