Emergency Use of Targeted Osmotic Lysis for the Treatment of a Patient with Aggressive Late-Stage Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Cervix
- PMID: 34201380
- PMCID: PMC8293172
- DOI: 10.3390/curroncol28030196
Emergency Use of Targeted Osmotic Lysis for the Treatment of a Patient with Aggressive Late-Stage Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Cervix
Abstract
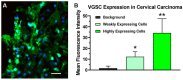
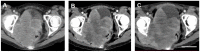
Upregulation of voltage-gated sodium channels (VGSCs) and Na+/K+-ATPase (sodium pumps) is common across most malignant carcinomas. Targeted osmotic lysis (TOL) is a developing technology in which the concomitant stimulation of VGSCs and pharmacological blockade of sodium pumps causes rapid selective osmotic lysis of carcinoma cells. This treatment of cervical carcinoma is evidence that TOL is a safe, well-tolerated and effective treatment for aggressive advanced carcinomas that has the potential to extend life without compromising its quality. TOL is likely to have broad application for the treatment of advanced-stage carcinomas.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01414608.
Keywords: advanced-stage cervical cancer; sodium channels; sodium pumps; targeted osmotic lysis.
Conflict of interest statement
D.P., P.R.M. and H.J.G.III are cofounders and managing members of Oleander Medical Technologies LLC.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Targeted Osmotic Lysis: A Novel Approach to Targeted Cancer Therapies.Biomedicines. 2022 Apr 2;10(4):838. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10040838. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35453588 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted Osmotic Lysis of Highly Invasive Breast Carcinomas Using Pulsed Magnetic Field Stimulation of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels and Pharmacological Blockade of Sodium Pumps.Cancers (Basel). 2020 May 31;12(6):1420. doi: 10.3390/cancers12061420. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32486340 Free PMC article.
-
Selective lysis of breast carcinomas by simultaneous stimulation of sodium channels and blockade of sodium pumps.Oncotarget. 2018 Feb 26;9(21):15606-15615. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.24581. eCollection 2018 Mar 20. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 29643996 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Targeted Osmotic Lysis in the Treatment of Advanced Carcinoma in Companion Animals: A Case Series.Case Rep Vet Med. 2022 Aug 2;2022:2747108. doi: 10.1155/2022/2747108. eCollection 2022. Case Rep Vet Med. 2022. PMID: 35967596 Free PMC article.
-
Voltage-gated Sodium Channels in Sensory Information Processing.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2019;18(4):273-278. doi: 10.2174/1871527317666180627114849. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2019. PMID: 29952271 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeted Osmotic Lysis: A Novel Approach to Targeted Cancer Therapies.Biomedicines. 2022 Apr 2;10(4):838. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10040838. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35453588 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer as a Channelopathy-Appreciation of Complimentary Pathways Provides a Different Perspective for Developing Treatments.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Sep 23;14(19):4627. doi: 10.3390/cancers14194627. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36230549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macromolecular Structure of Linearly Arranged Eukaryotic Chromosomes.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 22;23(16):9503. doi: 10.3390/ijms23169503. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36012767 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plant Compounds Inhibit the Growth of W12 Cervical Precancer Cells Containing Episomal or Integrant HPV DNA; Tanshinone IIA Synergizes with Curcumin in Cervical Cancer Cells.Viruses. 2024 Dec 31;17(1):55. doi: 10.3390/v17010055. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39861845 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Paul D., Maggi P., Piero F.D., Scahill S.D., Sherman K.J., Edenfield S., Gould H.J., 3rd Targeted osmotic lysis of highly invasive breast carcinomas using a pulsed magnetic field and pharmacological blockade of voltage-gated sodium channels. Cancers. 2020;12:1420. doi: 10.3390/cancers12061420. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Burke R.C., Bardet S.M., Carr L., Romanenko S., Arnaud-Cormos D., Leveque P., O’Connor R.P. Nanosecond pulsed electric fields depolarize transmembrane potential via voltage-gated K+, Ca2+ and TRPM8 channels in U87 glioblastoma cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2017;1859:2040–2050. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2017.07.004. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fraser S.P., Diss J.K.J., Chioni A.M., Mycielska M.E., Pan H., Yamaci R.F., Pani F., Siwy Z., Krasowska M., Grzywna Z., et al. Voltage-gated sodium channel expression and potentiation of human breast cancer metastasis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005;11:5381–5389. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0327. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fraser S.P., Ozerlat-Gunduz I., Brackenbury W.J., Fitzgerald E.M., Campbell T.M., Coombes R.C., Djamgoz M.B.A. Regulation of voltage-gated sodium channel expression in cancer: Hormones, growth factors and auto-regulation. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2014;369:20130105. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0105. - DOI - PMC - PubMed

