Identification of Volatile Sulfur Compounds Produced by Schizophyllum commune
- PMID: 34201392
- PMCID: PMC8226890
- DOI: 10.3390/jof7060465
Identification of Volatile Sulfur Compounds Produced by Schizophyllum commune
Abstract
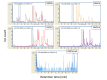
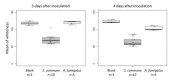
Schizophyllum commune is a causative agent of allergic bronchopulmonary mycosis, allergic fungal rhinosinusitis, and basidiomycosis. Diagnosis of these diseases remains difficult because no commercially available tool exists to identify the pathogen. Unique volatile organic compounds produced by a pathogen might be useful for non-invasive diagnosis. Here, we explored microbial volatile organic compounds produced by S. commune. Volatile sulfur compounds, dimethyl disulfide (48 of 49 strains) and methyl ethyl disulfide (49 of 49 strains), diethyl disulfide (34 of 49 strains), dimethyl trisulfide (40 of 49 strains), and dimethyl tetrasulfide (32 of 49 strains) were detected from headspace air in S. commune cultured vials. Every S. commune strain produced at least one volatile sulfur compound analyzed in this study. Those volatile sulfur compounds were not detected from the cultures of Aspergillus spp. (A. fumigatus, A. flavus, A. niger, and A. terreus), which are other major causative agents of allergic bronchopulmonary mycosis. The last, we examined H2S detection using lead acetate paper. Headspace air from S. commune rapidly turned the lead acetate paper black. These results suggest that those volatile sulfur compounds are potent targets for the diagnosis of S. commune and infectious diseases.
Keywords: Schizophyllum commune; allergic bronchopulmonary mycosis; microbial volatile organic compounds; volatile sulfur compounds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Allergic bronchopulmonary mycosis in Schizophyllum commune with positive Aspergillus-specific IgE antibodies: A case report.Respirol Case Rep. 2024 Jul 16;12(7):e01433. doi: 10.1002/rcr2.1433. eCollection 2024 Jul. Respirol Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 39015483 Free PMC article.
-
Glucoamylase is a major allergen of Schizophyllum commune.Clin Exp Allergy. 2014 Mar;44(3):450-7. doi: 10.1111/cea.12260. Clin Exp Allergy. 2014. PMID: 24372664
-
Allergic bronchopulmonary mycosis caused by the basidiomycetous fungus Schizophyllum commune.Clin Infect Dis. 1994 Mar;18(3):305-9. doi: 10.1093/clinids/18.3.305. Clin Infect Dis. 1994. PMID: 8011808
-
[Mucoid impaction of the bronchi caused by Schizophyllum commune which developed after discontinuation of itraconazole administration].Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi. 2009 Apr;47(4):296-303. Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi. 2009. PMID: 19455959 Review. Japanese.
-
[Three cases of allergic bronchopulmonary mycosis due to Schizophyllum commune].Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi. 2010 Dec;48(12):912-7. Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi. 2010. PMID: 21226297 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Diversity and Antimicrobial Activity of Intestinal Fungi from Three Species of Coral Reef Fish.J Fungi (Basel). 2023 May 26;9(6):613. doi: 10.3390/jof9060613. J Fungi (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37367549 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical characteristics of allergic bronchopulmonary mycosis caused by Schizophyllum commune.Clin Transl Allergy. 2024 Jan;14(1):e12327. doi: 10.1002/clt2.12327. Clin Transl Allergy. 2024. PMID: 38282191 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

