Development of a Fast and Robust UHPLC Method for Apixaban In-Process Control Analysis
- PMID: 34201410
- PMCID: PMC8226502
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26123505
Development of a Fast and Robust UHPLC Method for Apixaban In-Process Control Analysis
Abstract
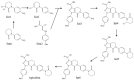
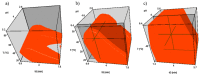
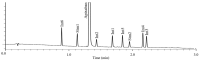
In-process control (IPC) is an important task during chemical syntheses in pharmaceutical industry. Despite the fact that each chemical reaction is unique, the most common analytical technique used for IPC analysis is high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Today, the so-called "Quality by Design" (QbD) principle is often being applied rather than "Trial and Error" approach for HPLC method development. The QbD approach requires only for a very few experimental measurements to find the appropriate stationary phase and optimal chromatographic conditions such as the composition of mobile phase, gradient steepness or time (tG), temperature (T), and mobile phase pH. In this study, the applicability of a multifactorial liquid chromatographic optimization software was studied in an extended knowledge space. Using state-of-the-art ultra-high performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC), the analysis time can significantly be shortened. By using UHPLC, it is possible to analyse the composition of the reaction mixture within few minutes. In this work, a mixture of route of synthesis of apixaban was analysed on short narrow bore column (50 × 2.1 mm, packed with sub-2 µm particles) resulting in short analysis time. The aim of the study was to cover a relatively narrow range of method parameters (tG, T, pH) in order to find a robust working point (zone). The results of the virtual (modeled) robustness testing were systematically compared to experimental measurements and Design of Experiments (DoE) based predictions.
Keywords: apixaban; design of experiments; liquid chromatography; method development; quality by design; robustness.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Simultaneous optimization of mobile phase composition and pH using retention modeling and experimental design.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018 Oct 25;160:336-343. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2018.07.054. Epub 2018 Aug 2. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018. PMID: 30114612
-
Stability-indicating RP-HPLC method development and validation for determination of nine impurities in apixaban tablet dosage forms. Robustness study by quality by design approach.Biomed Chromatogr. 2020 Jan;34(1):e4719. doi: 10.1002/bmc.4719. Epub 2019 Nov 19. Biomed Chromatogr. 2020. PMID: 31634417
-
Improved quality-by-design compliant methodology for method development in reversed-phase liquid chromatography.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2013 Oct;84:215-23. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2013.06.013. Epub 2013 Jun 21. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2013. PMID: 23850937
-
UHPLC method for multiproduct pharmaceutical analysis by Quality-by-Design.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018 Jan 30;148:361-368. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2017.10.014. Epub 2017 Oct 16. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018. PMID: 29111491
-
Enhancing Pharmaceutical Analysis with Analytical Quality by Design in UHPLC: A Review of Methodological Innovations (2014-2025).Crit Rev Anal Chem. 2025 Jun 12:1-21. doi: 10.1080/10408347.2025.2516607. Online ahead of print. Crit Rev Anal Chem. 2025. PMID: 40503695 Review.
Cited by
-
Analytical Method Development for 19 Alkyl Halides as Potential Genotoxic Impurities by Analytical Quality by Design.Molecules. 2022 Jul 11;27(14):4437. doi: 10.3390/molecules27144437. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35889310 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of Bupropion and Its Impurities via a Chaotropic Chromatography Method Following Analytical Quality-by-Design Principles for Method Development.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Sep 28;15(10):1196. doi: 10.3390/ph15101196. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36297308 Free PMC article.
References
-
- International Council for Harmonisation Guideline Q8 (R2) on Pharmaceutical Devlopment, Step 5 Version 2017. [(accessed on 22 June 2017)]; Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/internationa....
-
- Rácz N., Kormány R. Retention Modeling in an Extended Knowledge Space. Chromatographia. 2018;81:585–594. doi: 10.1007/s10337-017-3466-0. - DOI
-
- Fekete S., Molnár I., editors. Software-Assisted Method Development in High Performance Liquid Chromatography. World Scientific; Singapore: 2018.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

