Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Helicobacter pylori Eradication Regimens in Lithuania during the Years 2013-2020: Data from the European Registry on Helicobacter pylori Management (Hp-EuReg)
- PMID: 34201428
- PMCID: PMC8305910
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina57070642
Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Helicobacter pylori Eradication Regimens in Lithuania during the Years 2013-2020: Data from the European Registry on Helicobacter pylori Management (Hp-EuReg)
Abstract
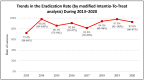
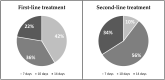
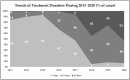
Background and Objectives: The prevalence of H. pylori in Eastern Europe remains quite high; however, there is insufficient data on the eradication regimens and their effectiveness. Therefore, the objective of the study was to evaluate the diagnostic methods and treatment of H. pylori infection as well as their adherence to Maastricht V/Florence consensus during the years 2013-2020 in Lithuania. Materials and Methods: Sub-study of the "European Registry on H. pylori Management" (Hp-EuReg), international multicenter prospective non-interventional registry of the routine clinical practice. Lithuanian data from the years 2013-2020 were analyzed for effectiveness on a modified intention-to-treat (mITT) basis. 2000 adult patients, diagnosed with H. pylori infection, were included. Data were compared to the European Maastricht V guidelines. Results: Triple-therapy was used in 90% of the cases. In 91% of the first-line prescriptions, standard triple therapy (STT) was used. The most common second-line treatment was a combination of PPI, amoxicillin and levofloxacin (PPI+A+L) (47%). The overall effectiveness in 552 cases valid for analysis was 90% by mITT. In first-line treatment, the STT effectiveness was 90% and second-line treatment with PPI+A+L achieved 92% by mITT. Increasing overall H. pylori eradication rates were observed: from 72% in 2013 to more than 90% in 2018-2020, as well as a shift from 7 to 10-14 days treatments duration throughout 2013-2020. Conclusions: In Lithuania, the prescribed eradication regimens for H. pylori were in accordance with the international guidelines but diagnostic methods and treatment duration only partially met Maastricht V/Florence guidelines. The eradication effectiveness was improved progressively during the years 2018-2020, reaching ≥90% cure rates.
Keywords: Helicobacter pylori; Hp-EuReg; Lithuania; effectiveness; eradication.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Effectiveness of empirical Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy with furazolidone in Russia: results from the European Registry on Helicobacter pylori Management (Hp-EuReg)].Ter Arkh. 2023 Mar 30;95(2):120-129. doi: 10.26442/00403660.2023.02.202107. Ter Arkh. 2023. PMID: 37167127 Russian.
-
First-Line Therapy for Helicobacter pylori in Slovenia: Data From 2013 to 2023 of the European Registry on H. pylori Management.Helicobacter. 2025 Mar-Apr;30(2):e70029. doi: 10.1111/hel.70029. Helicobacter. 2025. PMID: 40178062
-
Current Trends in the Management of Helicobacter pylori Infection in Serbia: Preliminary Results from the European Registry on H. pylori Management.Dig Dis. 2023;41(3):377-386. doi: 10.1159/000528389. Epub 2022 Dec 20. Dig Dis. 2023. PMID: 37253341
-
Standard triple therapy in Helicobacter pylori eradication in Turkey: Systematic evaluation and meta-analysis of 10-year studies.Turk J Gastroenterol. 2019 May;30(5):420-435. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2019.18693. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31060997 Free PMC article.
-
Safety profile of Helicobacter pylori eradication treatments: literature review and updated data of the European Registry on Helicobacter pylori management (Hp-EuReg).Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2024 May;23(5):553-564. doi: 10.1080/14740338.2024.2338245. Epub 2024 Apr 3. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2024. PMID: 38557327 Review.
Cited by
-
Helicobacter pylori Seroprevalence and Its Associations with Sociodemographic Characteristics, Environmental Factors, and Gastrointestinal Complaints: A Cross-Sectional Study in the Adult Population of Kaunas City, Lithuania.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 Jun 6;61(6):1049. doi: 10.3390/medicina61061049. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 40572737 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

