Epileptic Seizure Detection on an Ultra-Low-Power Embedded RISC-V Processor Using a Convolutional Neural Network
- PMID: 34201480
- PMCID: PMC8301882
- DOI: 10.3390/bios11070203
Epileptic Seizure Detection on an Ultra-Low-Power Embedded RISC-V Processor Using a Convolutional Neural Network
Abstract
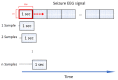
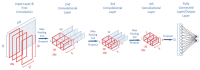
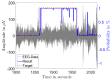
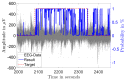
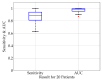
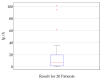
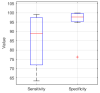
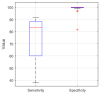
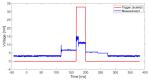
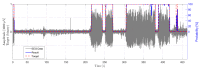
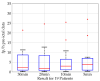
The treatment of refractory epilepsy via closed-loop implantable devices that act on seizures either by drug release or electrostimulation is a highly attractive option. For such implantable medical devices, efficient and low energy consumption, small size, and efficient processing architectures are essential. To meet these requirements, epileptic seizure detection by analysis and classification of brain signals with a convolutional neural network (CNN) is an attractive approach. This work presents a CNN for epileptic seizure detection capable of running on an ultra-low-power microprocessor. The CNN is implemented and optimized in MATLAB. In addition, the CNN is also implemented on a GAP8 microprocessor with RISC-V architecture. The training, optimization, and evaluation of the proposed CNN are based on the CHB-MIT dataset. The CNN reaches a median sensitivity of 90% and a very high specificity over 99% corresponding to a median false positive rate of 6.8 s per hour. After implementation of the CNN on the microcontroller, a sensitivity of 85% is reached. The classification of 1 s of EEG data takes t=35 ms and consumes an average power of P≈140 μW. The proposed detector outperforms related approaches in terms of power consumption by a factor of 6. The universal applicability of the proposed CNN based detector is verified with recording of epileptic rats. This results enable the design of future medical devices for epilepsy treatment.
Keywords: EEG; RISC-V; convolutional neural network; epileptic seizure detection; ultra-low-power.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization Epilepsy: Key Facts. [(accessed on 21 June 2021)];2019 Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/epilepsy.
-
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke . Epilepsy: Hope Through Research. Volume 15 NIH Publication; Bethesda, MD, USA: 2015.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

