Common Carotid Artery Volume Flow: A Comparison Study between Ultrasound Vector Flow Imaging and Phase Contrast Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- PMID: 34201493
- PMCID: PMC8293467
- DOI: 10.3390/neurolint13030028
Common Carotid Artery Volume Flow: A Comparison Study between Ultrasound Vector Flow Imaging and Phase Contrast Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Abstract
Volume flow estimation in the common carotid artery (CCA) can assess the absolute hemodynamic effect of a carotid stenosis. The aim of this study was to compare a commercial vector flow imaging (VFI) setup against the reference method magnetic resonance phase contrast angiography (MRA) for volume flow estimation in the CCA. Ten healthy volunteers were scanned with VFI and MRA over the CCA. VFI had an improved precision of 19.2% compared to MRA of 31.9% (p = 0.061). VFI estimated significantly lower volume flow than MRA (mean difference: 63.2 mL/min, p = 0.017), whilst the correlation between VFI and MRA was strong (R2 = 0.81, p < 0.0001). A Bland-Altman plot indicated a systematic bias. After bias correction, the percentage error was reduced from 41.0% to 25.2%. This study indicated that a VFI setup for volume flow estimation is precise and strongly correlated to MRA volume flow estimation, and after correcting for the systematic bias, VFI and MRA become interchangeable.
Keywords: common carotid artery; phase contrast magnetic resonance imaging; vector flow imaging; volume flow.
Conflict of interest statement
The author J.A.J. developed and patented the method Vector Flow Imaging and earns royalties for the selling of scanners with the Vector Flow Imaging option from BK medical. BK medical employs the authors J.B.O. and R.M. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

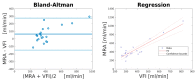
References
-
- Tanaka H., Watanabe Y., Nakamura H., Takahashi H., Arisawa A., Fujiwara T., Matsuo C., Tomiyama N. Multiple blood flow measurements before and after carotid artery stenting via phase-contrast magnetic resonance imaging: An observational study. PLoS ONE. 2018;13:e0195099. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0195099. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

