Hesperetin Nanocrystals Improve Mitochondrial Function in a Cell Model of Early Alzheimer Disease
- PMID: 34201544
- PMCID: PMC8300699
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox10071003
Hesperetin Nanocrystals Improve Mitochondrial Function in a Cell Model of Early Alzheimer Disease
Abstract
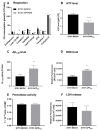
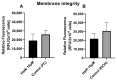
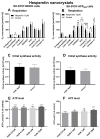
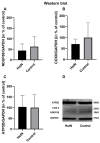
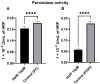
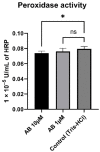
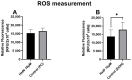
Mitochondrial dysfunction represents a hallmark of both brain aging and age-related neurodegenerative disorders including Alzheimer disease (AD). AD-related mitochondrial dysfunction is characterized by an impaired electron transport chain (ETC), subsequent decreased adenosine triphoshpate (ATP) levels, and elevated generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). The bioactive citrus flavanone hesperetin (Hst) is known to modulate inflammatory response, to function as an antioxidant, and to provide neuroprotective properties. The efficacy in improving mitochondrial dysfunction of Hst nanocrystals (HstN) with increased bioavailability has not yet been investigated. Human SH-SY5Y cells harboring neuronal amyloid precursor protein (APP695) acted as a model for the initial phase of AD. MOCK-transfected cells served as controls. The energetic metabolite ATP was determined using a luciferase-catalyzed bioluminescence assay. The activity of mitochondrial respiration chain complexes was assessed by high-resolution respirometry using a Clarke electrode. Expression levels of mitochondrial respiratory chain complex genes were determined using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). The levels of amyloid β-protein (Aβ1-40) were measured using homogeneous time-resolved fluorescence (HTRF). ROS levels, peroxidase activity, and cytochrome c activity were determined using a fluorescence assay. Compared to pure Hst dissolved in ethanol (HstP), SH-SY5Y-APP695 cells incubated with HstN resulted in significantly reduced mitochondrial dysfunction: ATP levels and respiratory chain complex activity significantly increased. Gene expression levels of RCC I, IV, and V were significantly upregulated. In comparison, the effects of HstN on SY5Y-MOCK control cells were relatively small. Pure Hst dissolved in ethanol (HstP) had almost no effect on both cell lines. Neither HstN nor HstP led to significant changes in Aβ1-40 levels. HstN and HstP were both shown to lower peroxidase activity significantly. Furthermore, HstN significantly reduced cytochrome c activity, whereas HstP had a significant effect on reducing ROS in SH-SY5Y-APP695 cells. Thus, it seems that the mechanisms involved may not be linked to altered Aβ production. Nanoflavonoids such as HstN have the potential to prevent mitochondria against dysfunction. Compared to its pure form, HstN showed a greater effect in combatting mitochondrial dysfunction. Further studies should evaluate whether HstN protects against age-related mitochondrial dysfunction and thus may contribute to late-onset AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer disease; ROS; amyloid beta; hesperetin; mitochondria; mitochondria dysfunction; nanoparticles; peroxidase activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Alzheimer’s Disease International . World Alzheimer Report 2019: Attitudes to Dementia. Alzheimer’s Disease International; London, UK: 2019.
-
- Barker W.W., Luis C.A., Kashuba A., Luis M., Harwood D.G., Loewenstein D., Waters C., Jimison P., Shepherd E., Sevush S., et al. Relative Frequencies of Alzheimer Disease, Lewy Body, Vascular and Frontotemporal Dementia, and Hippocampal Sclerosis in the State of Florida Brain Bank. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2002;16:203–212. doi: 10.1097/00002093-200210000-00001. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

