α-Synuclein Strains: Does Amyloid Conformation Explain the Heterogeneity of Synucleinopathies?
- PMID: 34201558
- PMCID: PMC8301881
- DOI: 10.3390/biom11070931
α-Synuclein Strains: Does Amyloid Conformation Explain the Heterogeneity of Synucleinopathies?
Abstract
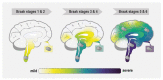
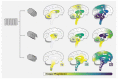
Synucleinopathies are a heterogeneous group of neurodegenerative diseases with amyloid deposits that contain the α-synuclein (SNCA/α-Syn) protein as a common hallmark. It is astonishing that aggregates of a single protein are able to give rise to a whole range of different disease manifestations. The prion strain hypothesis offers a possible explanation for this conundrum. According to this hypothesis, a single protein sequence is able to misfold into distinct amyloid structures that can cause different pathologies. In fact, a growing body of evidence suggests that conformationally distinct α-Syn assemblies might be the causative agents behind different synucleinopathies. In this review, we provide an overview of research on the strain hypothesis as it applies to synucleinopathies and discuss the potential implications for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
Keywords: alpha-synuclein; amyloid; conformational strains; prion-like propagation; prions; synucleinopathies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

