Medical Cost of Cancer Care for Privately Insured Children in Chile
- PMID: 34201571
- PMCID: PMC8267683
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph18136746
Medical Cost of Cancer Care for Privately Insured Children in Chile
Abstract
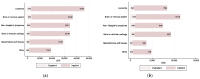
Medical care for children with cancer is complex and expensive, and represents a large financial burden for families around the world. We estimated the medical cost of cancer care for children under the age of 18, using administrative records of the universe of children with private insurance in Chile in the period 2007-2018, based on a sample of 3853 observations. We analyzed total cost and out-of-pocket spending by patients' characteristics, type of cancer, and by service. Children with cancer had high annual medical costs, USD 32,287 on average for 2018. Costs were higher for the younger children in the sample. The vast majority of the cost was driven by inpatient hospital care for all types of cancer. The average total cost increased 20% in real terms over the period of study, while out-of-pocket expenses increased almost 29%. Private insurance beneficiaries faced a significant economic burden associated with medical treatment of a child with cancer. Interventions that reduce hospitalizations, as well as systemwide reforms that incorporate maximum out-of-pocket payments and prevent catastrophic expenditures, can contribute to alleviating the financial burden of childhood cancer.
Keywords: administrative data; childhood cancer; medical cost.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Departamento de Epidemiologia Ministerio de Salud . Primer Informe del Registro Nacional de Cáncer Infantil de Chile (Menores de 15 Años), RENCI. Departamento de Epidemiologia Ministerio de Salud; Santiago, Chile: 2018.
-
- Merrill C.T., Nagamine M., Hambrick M.M. Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) Statistical Briefs [Internet] Volume 37. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; Rockville, MD, USA: 2007. [(accessed on 20 January 2021)]. Pediatric Hospital Stays for Cancer, 2005. Available online: http://www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/reports/statbriefs/sb37.pdf.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

