Treatment with the Bacterial Toxin CNF1 Selectively Rescues Cognitive and Brain Mitochondrial Deficits in a Female Mouse Model of Rett Syndrome Carrying a MeCP2-Null Mutation
- PMID: 34201747
- PMCID: PMC8269120
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22136739
Treatment with the Bacterial Toxin CNF1 Selectively Rescues Cognitive and Brain Mitochondrial Deficits in a Female Mouse Model of Rett Syndrome Carrying a MeCP2-Null Mutation
Abstract
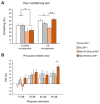
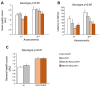
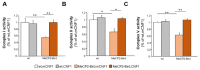
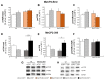
Rett syndrome (RTT) is a rare neurological disorder caused by mutations in the X-linked MECP2 gene and a major cause of intellectual disability in females. No cure exists for RTT. We previously reported that the behavioural phenotype and brain mitochondria dysfunction are widely rescued by a single intracerebroventricular injection of the bacterial toxin CNF1 in a RTT mouse model carrying a truncating mutation of the MeCP2 gene (MeCP2-308 mice). Given the heterogeneity of MECP2 mutations in RTT patients, we tested the CNF1 therapeutic efficacy in a mouse model carrying a null mutation (MeCP2-Bird mice). CNF1 selectively rescued cognitive defects, without improving other RTT-related behavioural alterations, and restored brain mitochondrial respiratory chain complex activity in MeCP2-Bird mice. To shed light on the molecular mechanisms underlying the differential CNF1 effects on the behavioural phenotype, we compared treatment effects on relevant signalling cascades in the brain of the two RTT models. CNF1 provided a significant boost of the mTOR activation in MeCP2-308 hippocampus, which was not observed in the MeCP2-Bird model, possibly explaining the differential effects of CNF1. These results demonstrate that CNF1 efficacy depends on the mutation beared by MeCP2-mutated mice, stressing the need of testing potential therapeutic approaches across RTT models.
Keywords: Rett syndrome; Rho GTPases; behaviour; cognition; energy metabolism; mTOR; mitochondria; mouse models.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Valenti D., de Bari L., De Filippis B., Henrion-Caude A., Vacca R.A. Mitochondrial dysfunction as a central actor in intellectual disability-related diseases: An overview of Down syndrome, autism, Fragile X and Rett syndrome. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2014;46:202–217. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2014.01.012. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

