The C-Terminal Domain of LRRK2 with the G2019S Substitution Increases Mutant A53T α-Synuclein Toxicity in Dopaminergic Neurons In Vivo
- PMID: 34201785
- PMCID: PMC8268201
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22136760
The C-Terminal Domain of LRRK2 with the G2019S Substitution Increases Mutant A53T α-Synuclein Toxicity in Dopaminergic Neurons In Vivo
Abstract
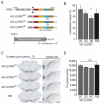
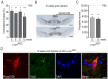
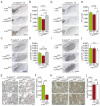
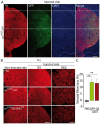
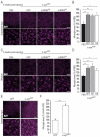
Alpha-synuclein (α-syn) and leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) play crucial roles in Parkinson's disease (PD). They may functionally interact to induce the degeneration of dopaminergic (DA) neurons via mechanisms that are not yet fully understood. We previously showed that the C-terminal portion of LRRK2 (ΔLRRK2) with the G2019S mutation (ΔLRRK2G2019S) was sufficient to induce neurodegeneration of DA neurons in vivo, suggesting that mutated LRRK2 induces neurotoxicity through mechanisms that are (i) independent of the N-terminal domains and (ii) "cell-autonomous". Here, we explored whether ΔLRRK2G2019S could modify α-syn toxicity through these two mechanisms. We used a co-transduction approach in rats with AAV vectors encoding ΔLRRK2G2019S or its "dead" kinase form, ΔLRRK2DK, and human α-syn with the A53T mutation (AAV-α-synA53T). Behavioral and histological evaluations were performed at 6- and 15-weeks post-injection. Results showed that neither form of ΔLRRK2 alone induced the degeneration of neurons at these post-injection time points. By contrast, injection of AAV-α-synA53T alone resulted in motor signs and degeneration of DA neurons. Co-injection of AAV-α-synA53T with AAV-ΔLRRK2G2019S induced DA neuron degeneration that was significantly higher than that induced by AAV-α-synA53T alone or with AAV-ΔLRRK2DK. Thus, mutated α-syn neurotoxicity can be enhanced by the C-terminal domain of LRRK2G2019 alone, through cell-autonomous mechanisms.
Keywords: AAVs; Parkinson’s disease; cell-autonomous mechanisms; leucine-rich repeat kinase 2; α-synuclein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- rolling grants/Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique
- rolling grants/Commissariat à l'Énergie Atomique et aux Énergies Alternatives
- AAP 2010, Engt 00016819 and AAP 2014, Engt 2014-0052580/Fondation de France
- PhD extention grant 2016 and 2019/Association France Parkinson
- NeurATRIS, "Investissement d'Avenir", ANR-11-INBS-0011/Agence Nationale de la Recherche
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

