Towards Clean and Safe Water: A Review on the Emerging Role of Imprinted Polymer-Based Electrochemical Sensors
- PMID: 34201852
- PMCID: PMC8271813
- DOI: 10.3390/s21134300
Towards Clean and Safe Water: A Review on the Emerging Role of Imprinted Polymer-Based Electrochemical Sensors
Abstract
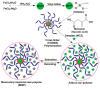
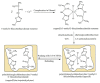
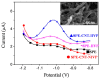
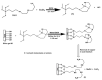
This review critically summarizes the knowledge of imprinted polymer-based electrochemical sensors for the detection of pesticides, metal ions and waterborne pathogenic bacteria, focusing on the last five years. MIP-based electrochemical sensors exhibit low limits of detection (LOD), high selectivity, high sensitivity and low cost. We put the emphasis on the design of imprinted polymers and their composites and coatings by radical polymerization, oxidative polymerization of conjugated monomers or sol-gel chemistry. Whilst most imprinted polymers are used in conjunction with differential pulse or square wave voltammetry for sensing organics and metal ions, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) appears as the chief technique for detecting bacteria or their corresponding proteins. Interestingly, bacteria could also be probed via their quorum sensing signaling molecules or flagella proteins. If much has been developed in the past decade with glassy carbon or gold electrodes, it is clear that carbon paste electrodes of imprinted polymers are more and more investigated due to their versatility. Shortlisted case studies were critically reviewed and discussed; clearly, a plethora of tricky strategies of designing selective electrochemical sensors are offered to "Imprinters". We anticipate that this review will be of interest to experts and newcomers in the field who are paying time and effort combining electrochemical sensors with MIP technology.
Keywords: bacteria; electrochemical sensors; imprinted polymers; metal ions; pesticides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures













References
-
- Stradiotto N.R., Yamanaka H., Zanoni M.V.B. Electrochemical sensors: A powerful tool in analytical chemistry. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2003;14:159–173. doi: 10.1590/S0103-50532003000200003. - DOI
-
- Branger C., Meouche W., Margaillan A. Recent advances on ion-imprinted polymers. React. Funct. Polym. 2013;73:859–875. doi: 10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2013.03.021. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

