Chronic Nonbacterial Osteomyelitis in Children
- PMID: 34202154
- PMCID: PMC8303960
- DOI: 10.3390/children8070551
Chronic Nonbacterial Osteomyelitis in Children
Abstract
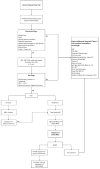
Chronic nonbacterial osteomyelitis (CNO) is an auto-inflammatory bone disorder with a wide spectrum of clinical manifestations, from unifocal to multifocal lesions. When it manifests with multifocal lesions, it is also referred to as chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis (CRMO). CNO/CRMO can affect all age groups, with the pediatric population being the most common. Patients may present with systemic inflammation, but there is no pathognomonic laboratory finding. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the gold standard radiological tool for diagnosis. In the absence of validated diagnostic criteria, CNO/CRMO remains an exclusion diagnosis. Bone biopsy does not show a specific disease pattern, but it may be necessary in unifocal or atypical cases to differentiate it from malignancy or infection. First-line treatments are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), while bisphosphonates or TNF-α blockers can be used in refractory cases. The disease course is unpredictable, and uncontrolled lesions can complicate with bone fractures and deformations, underlying the importance of long-term follow-up in these patients.
Keywords: DIRA; Majeed syndrome; PAPA syndrome; SAPHO; auto-inflammatory bone disease; chronic nonbacterial osteitis; chronic nonbacterial osteomyelitis (CNO); chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis (CRMO); monogenic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Giedion A., Holthusen W., Masel L.F., Vischer D. Subacute and chronic “symmetrical” osteomyelitis. Ann. Radiol. 1972;15:329–342. - PubMed
-
- Gamalero L., Belot A., Zajc Avramovic M., Giani T., Filocamo G., Guleria S., Ferrara G., Minoia F., Hofer M., Larbre J.-P., et al. Chronic non-bacterial osteomyelitis: A retrospective international study on clinical manifestations and response to treatment. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2020;38:1255. - PubMed
-
- Beck C., Morbach H., Beer M., Stenzel M., Tappe D., Gattenlöhner S., Hofmann U., Raab P., Girschick H.J. Chronic nonbacterial osteomyelitis in childhood: Prospective follow-up during the first year of anti-inflammatory treatment. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2010;12:R74. doi: 10.1186/ar2992. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

