Conserved Influenza Hemagglutinin, Neuraminidase and Matrix Peptides Adjuvanted with ALFQ Induce Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies
- PMID: 34202178
- PMCID: PMC8310080
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines9070698
Conserved Influenza Hemagglutinin, Neuraminidase and Matrix Peptides Adjuvanted with ALFQ Induce Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies
Abstract
A universal influenza candidate vaccine that targets multiple conserved influenza virus epitopes from hemagglutinin (HA), neuraminidase (NA) and matrix (M2e) proteins was combined with the potent Army liposomal adjuvant (ALFQ) to promote induction of broad immunity to seasonal and pandemic influenza strains. The unconjugated and CRM-conjugated composite peptides formulated with ALFQ were highly immunogenic and induced both humoral and cellular immune responses in mice. Broadly reactive serum antibodies were induced across various IgG isotypes. Mice immunized with the unconjugated composite peptide developed antibody responses earlier than mice immunized with conjugated peptides, and the IgG antibodies were broadly reactive and neutralizing across Groups 1 and 2 influenza viruses. Multi-epitope unconjugated influenza composite peptides formulated with ALFQ provide a novel strategy for the development of a universal influenza vaccine. These synthetic peptide vaccines avoid the pitfalls of egg-produced influenza vaccines and production can be scaled up rapidly and economically.
Keywords: ALFQ; QS21 (also known as QS-21); Th1/Th2 responses; broadly reactive antibodies; immune responses; influenza; liposomes; neutralizing antibodies; peptides; universal vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
Carl R. Alving is one of the two inventors on an issued ALFQ patent owned by the U.S. Army. Carl R. Alving and Gary R. Matyas are inventors of a patent application owned by the U.S. Army covering ALFQ formulated with a malaria antigen. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




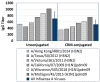

References
-
- World Health Organisation Influenza (Seasonal) [(accessed on 11 June 2021)]; Available online: http://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/influenza-(seasonal)
-
- World Health Organisation Cumulative Number of Confirmed Human Cases for Avian Influenza A(H5N1) Reported to WHO 2003–2020. [(accessed on 11 June 2020)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/influenza/human_animal_interface/2020_01_20_tableH5N....
-
- Chen Y.-Q., Wohlbold T.J., Zheng N.-Y., Huang M., Huang Y., Neu K.E., Lee J., Wan H., Rojas K.T., Kirkpatrick E., et al. Influenza Infection in Humans Induces Broadly Cross-Reactive and Protective Neuraminidase-Reactive Antibodies. Cell. 2018;173:417–429.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.03.030. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

