Clinicopathological and Genomic Profiles of Atypical Fibroxanthoma and Pleomorphic Dermal Sarcoma Identify Overlapping Signatures with a High Mutational Burden
- PMID: 34202213
- PMCID: PMC8303615
- DOI: 10.3390/genes12070974
Clinicopathological and Genomic Profiles of Atypical Fibroxanthoma and Pleomorphic Dermal Sarcoma Identify Overlapping Signatures with a High Mutational Burden
Abstract
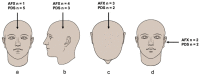
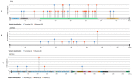
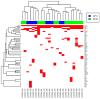
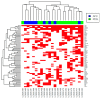
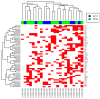
Atypical fibroxanthoma (AFX) and pleomorphic dermal sarcoma (PDS) are rare tumors developing in chronically sun-exposed skin. Clinicopathological features are similar, but they differ in prognosis, while PDS has a more aggressive course with a higher risk for local recurrence and metastases. In current clinical practice, they are diagnosed by exclusion using immunohistochemistry. Thus, stringent diagnostic criteria and correct differentiation are critical in management and treatment for optimal outcomes. This retrospective single-center study collected clinicopathological data and tumor samples of 10 AFX and 18 PDS. Extracted genomic DNA from tumor specimens was analyzed by a next-generation sequencing (NGS) platform (FoundationOne-CDx™). Among 65 identified mutations, TP53 inactivating mutations were observed in all tumor specimens. In both AFX and PDS, the known pathogenic gene alterations in CDKN2A, TERT promoter, and NOTCH1 were frequently present, along with high mutational burden and stable Micro-Satellite Instability status. The mutational profiles differed only in ASXL1, which was only present in AFX. Further differences were identified in likely pathogenic and unknown gene alterations. Similarities in their genomic signatures could help to distinguish them from other malignancies, but they are not distinguishable between each other using the FoundationOne-CDx™ NGS panel. Therefore, histological criteria to determine diagnosis remain valid. For further insight, performing deep tumor profiling may be necessary.
Keywords: atypical fibroxanthoma; next-generation sequencing; pleomorphic dermal sarcoma; tumor genomic profiling.
Conflict of interest statement
R.D. has intermittent, project-focused consulting and/or advisory relationships with No vartis, Merck Sharp & Dhome (MSD), Bristol-Myers Squibb (BMS), Roche, Amgen, Takeda, Pierre Fabre outside the submitted work. E.R. has intermittent, project-focused consulting relationships with Amgen, BMS, and Sanofi outside the submitted work. M.Z. has intermittent, project-focused relationships with F. Hoffmann-La Roche outside the submitted work. M.A., A.K., F.A. and P.T. had no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Atypical fibroxanthoma and pleomorphic dermal sarcoma harbor frequent NOTCH1/2 and FAT1 mutations and similar DNA copy number alteration profiles.Mod Pathol. 2018 Mar;31(3):418-428. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2017.146. Epub 2017 Nov 3. Mod Pathol. 2018. PMID: 29099504 Free PMC article.
-
Oncogene and therapeutic target analyses in atypical fibroxanthomas and pleomorphic dermal sarcomas.Oncotarget. 2016 Apr 19;7(16):21763-74. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7845. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26943575 Free PMC article.
-
Pleomorphic dermal sarcoma in a man with HIV: report with next-generation sequencing analysis and review of the atypical fibroxanthoma/pleomorphic dermal sarcoma spectrum.Dermatol Online J. 2019 Nov 15;25(11):13030/qt8p66q9fv. Dermatol Online J. 2019. PMID: 32045146 Review.
-
A genomic survey of sarcomas on sun-exposed skin reveals distinctive candidate drivers and potentially targetable mutations.Hum Pathol. 2020 Aug;102:60-69. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2020.06.003. Epub 2020 Jun 12. Hum Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32540221
-
Pleomorphic Dermal Sarcoma.Surg Pathol Clin. 2024 Mar;17(1):153-158. doi: 10.1016/j.path.2023.06.007. Epub 2023 Aug 5. Surg Pathol Clin. 2024. PMID: 38278604 Review.
Cited by
-
Single-cell and spatial transcriptomics identify COL6A3 as a prognostic biomarker in undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma.Mol Cancer. 2024 Nov 15;23(1):257. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02168-8. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39548577 Free PMC article.
-
Glycolysis-Related LINC02432/Hsa-miR-98-5p/HK2 Axis Inhibits Ferroptosis and Predicts Immune Infiltration, Tumor Mutation Burden, and Drug Sensitivity in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jun 20;13:937413. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.937413. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35795552 Free PMC article.
-
Retrospective Single-Center Case Study of Clinical Variables and the Degree of Actinic Elastosis Associated with Rare Skin Cancers.Biology (Basel). 2024 Jul 16;13(7):529. doi: 10.3390/biology13070529. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39056721 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Characterization of Atypical Fibroxanthoma and Pleomorphic Dermal Sarcoma.Cancers (Basel). 2025 May 27;17(11):1785. doi: 10.3390/cancers17111785. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40507266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Keloidal atypical fibroxanthoma of the scalp.BMJ Case Rep. 2023 Nov 16;16(11):e258025. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2023-258025. BMJ Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 37973539
References
-
- Koch M., Freundl A.J., Agaimy A., Kiesewetter F., Kunzel J., Cicha I., Alexiou C. Atypical Fibroxanthoma–Histological Diagnosis, Immunohistochemical Markers and Concepts of Therapy. Anticancer Res. 2015;35:5717–5735. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

