Complement System and Potential Therapeutics in Age-Related Macular Degeneration
- PMID: 34202223
- PMCID: PMC8269056
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22136851
Complement System and Potential Therapeutics in Age-Related Macular Degeneration
Abstract
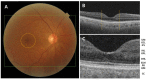
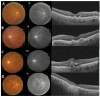
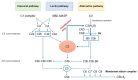
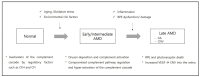
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a complex multifactorial disease characterized in its late form by neovascularization (wet type) or geographic atrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium cell layer (dry type). The complement system is an intrinsic component of innate immunity. There has been growing evidence that the complement system plays an integral role in maintaining immune surveillance and homeostasis in AMD. Based on the association between the genotypes of complement variants and AMD occurrence and the presence of complement in drusen from AMD patients, the complement system has become a therapeutic target for AMD. However, the mechanism of complement disease propagation in AMD has not been fully understood. This concise review focuses on an overall understanding of the role of the complement system in AMD and its ongoing clinical trials. It provides further insights into a strategy for the treatment of AMD targeting the complement system.
Keywords: age-related macular degeneration; clinical trial; complement cascade; therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wong W.L., Su X., Li X., Cheung C.M., Klein R., Cheng C.Y., Wong T.Y. Global prevalence of age-related macular degeneration and disease burden projection for 2020 and 2040: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob. Health. 2014;2:e106–e116. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(13)70145-1. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

