Fe65: A Scaffolding Protein of Actin Regulators
- PMID: 34202290
- PMCID: PMC8304848
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10071599
Fe65: A Scaffolding Protein of Actin Regulators
Abstract
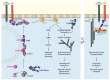
The scaffolding protein family Fe65, composed of Fe65, Fe65L1, and Fe65L2, was identified as an interaction partner of the amyloid precursor protein (APP), which plays a key function in Alzheimer's disease. All three Fe65 family members possess three highly conserved interaction domains, forming complexes with diverse binding partners that can be assigned to different cellular functions, such as transactivation of genes in the nucleus, modulation of calcium homeostasis and lipid metabolism, and regulation of the actin cytoskeleton. In this article, we rule out putative new intracellular signaling mechanisms of the APP-interacting protein Fe65 in the regulation of actin cytoskeleton dynamics in the context of various neuronal functions, such as cell migration, neurite outgrowth, and synaptic plasticity.
Keywords: Arf6; Arp2/3; DOCK; ELMO; Mena; Rac; Tip60; cortactin; neurite outgrowth; structural synaptic plasticity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Bressler S.L., Gray M.D., Sopher B.L., Hu Q., Hearn M.G., Pham D.G., Dinulos M.B., Fukuchi K., Sisodia S.S., Miller M.A., et al. cDNA cloning and chromosome mapping of the human Fe65 gene: Interaction of the conserved cytoplasmic domains of the human beta-amyloid precursor protein and its homologues with the mouse Fe65 protein. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1996;5:1589–1598. doi: 10.1093/hmg/5.10.1589. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Blanco G., Irving N.G., Brown S.D., Miller C.C., McLoughlin D.M. Mapping of the human and murine X11-like genes (APBA2 and apba2), the murine Fe65 gene (Apbb1), and the human Fe65-like gene (APBB2): Genes encoding phosphotyrosine-binding domain proteins that interact with the Alzheimer’s disease amyloid precursor protein. Mamm. Genome. 1998;9:473–475. doi: 10.1007/s003359900800. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fiore F., Zambrano N., Minopoli G., Donini V., Duilio A., Russo T. The regions of the Fe65 protein homologous to the phosphotyrosine interaction/phosphotyrosine binding domain of Shc bind the intracellular domain of the Alzheimer’s amyloid precursor protein. J. Biol. Chem. 1995;270:30853–30856. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.52.30853. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

