Discovery of Novel Chemical Series of OXA-48 β-Lactamase Inhibitors by High-Throughput Screening
- PMID: 34202402
- PMCID: PMC8308845
- DOI: 10.3390/ph14070612
Discovery of Novel Chemical Series of OXA-48 β-Lactamase Inhibitors by High-Throughput Screening
Abstract
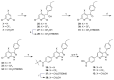
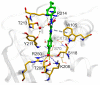
The major cause of bacterial resistance to β-lactams is the production of hydrolytic β-lactamase enzymes. Nowadays, the combination of β-lactam antibiotics with β-lactamase inhibitors (BLIs) is the main strategy for overcoming such issues. Nevertheless, particularly challenging β-lactamases, such as OXA-48, pose the need for novel and effective treatments. Herein, we describe the screening of a proprietary compound collection against Klebsiella pneumoniae OXA-48, leading to the identification of several chemotypes, like the 4-ideneamino-4H-1,2,4-triazole (SC_2) and pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridine (SC_7) cores as potential inhibitors. Importantly, the most potent representative of the latter series (ID2, AC50 = 0.99 μM) inhibited OXA-48 via a reversible and competitive mechanism of action, as demonstrated by biochemical and X-ray studies; furthermore, it slightly improved imipenem's activity in Escherichia coli ATCC BAA-2523 β-lactam resistant strain. Also, ID2 showed good solubility and no sign of toxicity up to the highest tested concentration, resulting in a promising starting point for further optimization programs toward novel and effective non-β-lactam BLIs.
Keywords: HTS; OXA-48; bacterial resistance; β-lactamase inhibitor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures














References
-
- Abraham E.P., Chain E. An enzyme from bacteria able to destroy penicillin. 1940. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1988;10:677–678. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

