Waste Glass in Cement and Geopolymer Concretes: A Review on Durability and Challenges
- PMID: 34202421
- PMCID: PMC8271587
- DOI: 10.3390/polym13132071
Waste Glass in Cement and Geopolymer Concretes: A Review on Durability and Challenges
Erratum in
-
Correction: Siddika et al. Waste Glass in Cement and Geopolymer Concretes: A Review on Durability and Challenges. Polymers 2021, 13, 2071.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Mar 8;14(6):1068. doi: 10.3390/polym14061068. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35335601 Free PMC article.
Abstract
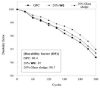
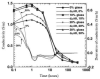
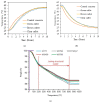
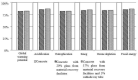
Every year, the world is producing around 100 million tons of waste glass (WG), the majority of them are going to landfills that create massive environmental problems. One approach to solve this problem is to transform waste glass into construction materials. Glass is recyclable; however, the melting temperature of the glass is highly dependent on its colour that requires sorting before recycling. To overcome this challenge, many researchers and end-users are using broken glass in concrete either as a binder or aggregates. While significant investigations have done in this area, however, the outcomes of these studies are scattered, and difficult to reach a firm conclusion about the effectiveness of WG in concrete. In this study, the roles of WG and its impact on microstructural and durability properties for both cement and geopolymer concrete are critically reviewed. This review reveals that the amorphous silica in WG effectively participate to the hydration and geopolymerization process and improve concrete microstructural properties. This behaviour of WG help to produce durable concrete against shrinkage, chemical attack, freeze-thaw action, electrical and thermal insulation properties. The optimum replacement volume of binders or natural aggregates and particle size of WG need to be selected carefully to minimise the possible alkali-silica reaction. This review discusses a wide range of parameters for durability properties and challenges associated with WG concrete, which provides necessary guidelines for best practice with future research directions.
Keywords: activator; aggregate; alkali-activated cement; challenges; durability; waste glass.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Bahoria B.V., Parbat D.K., Nagarnaik P.B. Materials Today: Proceedings. Volume 5. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2018. XRD Analysis of Natural sand, Quarry dust, waste plastic (ldpe) to be used as a fine aggregate in concrete; pp. 1432–1438.
-
- Islam M.T., Islam M., Siddika A., Mamun M.A. Al Performance of rubberized concrete exposed to chloride solution and continuous wet–dry cycle. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2021;6:67. doi: 10.1007/s41062-020-00451-3. - DOI
-
- Siddika A., Amin M.R., Rayhan M.A., Islam M.S., Al Mamun M.A., Alyousef R., Amran Y.H.M. Performance of sustainable green concrete incorporated with fly ash rice husk ash and stone dust. Acta Polytech. 2021;61:279–291. doi: 10.14311/AP.2021.61.0279. - DOI
-
- Siddika A., Al Mamun M.A., Alyousef R., Mohammadhosseini H. State-of-the-art-review on rice husk ash: A supplementary cementitious material in concrete. J. King Saud Univ. Eng. Sci. 2021;33:294–307. doi: 10.1016/j.jksues.2020.10.006. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

