Comprehensive Survey of Using Machine Learning in the COVID-19 Pandemic
- PMID: 34202587
- PMCID: PMC8303306
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics11071155
Comprehensive Survey of Using Machine Learning in the COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
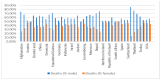
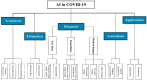
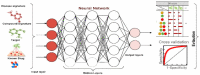
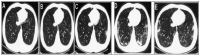
Since December 2019, the global health population has faced the rapid spreading of coronavirus disease (COVID-19). With the incremental acceleration of the number of infected cases, the World Health Organization (WHO) has reported COVID-19 as an epidemic that puts a heavy burden on healthcare sectors in almost every country. The potential of artificial intelligence (AI) in this context is difficult to ignore. AI companies have been racing to develop innovative tools that contribute to arm the world against this pandemic and minimize the disruption that it may cause. The main objective of this study is to survey the decisive role of AI as a technology used to fight against the COVID-19 pandemic. Five significant applications of AI for COVID-19 were found, including (1) COVID-19 diagnosis using various data types (e.g., images, sound, and text); (2) estimation of the possible future spread of the disease based on the current confirmed cases; (3) association between COVID-19 infection and patient characteristics; (4) vaccine development and drug interaction; and (5) development of supporting applications. This study also introduces a comparison between current COVID-19 datasets. Based on the limitations of the current literature, this review highlights the open research challenges that could inspire the future application of AI in COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID_19; artificial intelligence; deep learning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Bin S.Y., Heo J.Y., Song M.-S., Lee J., Kim E.-H., Park S.-J., Kwon H.-I., Kim S.M., Kim Y.-I., Si Y.-J., et al. Environmental Contamination and Viral Shedding in MERS Patients during MERS-CoV Outbreak in South Korea. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015;62:755–760. doi: 10.1093/cid/civ1020. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

