Palmitoylethanolamide/Baicalein Regulates the Androgen Receptor Signaling and NF-κB/Nrf2 Pathways in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- PMID: 34202665
- PMCID: PMC8300753
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox10071014
Palmitoylethanolamide/Baicalein Regulates the Androgen Receptor Signaling and NF-κB/Nrf2 Pathways in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Abstract
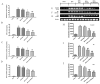
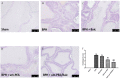
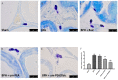
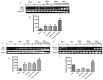
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is the most common benign tumor in males. Androgen/androgen receptor (AR) signaling plays a key role in the development of BPH; its alterations cause an imbalance between prostate cell growth and apoptosis. Furthermore, chronic inflammation and oxidative stress, which are common conditions in BPH, contribute to disrupting the homeostasis between cell proliferation and cell death. With this background in mind, we investigated the effect of ultramicronized palmitoylethanolamide (um-PEA), baicalein (Baic) and co-ultramicronized um-PEA/Baic in a fixed ratio of 10:1 in an experimental model of BPH. BPH was induced in rats by daily administration of testosterone propionate (3 mg/kg) for 14 days. Baic (1 mg/kg), um-PEA (9 mg/kg) and um-PEA/Baic (10 mg/kg) were administered orally every day for 14 days. This protocol led to alterations in prostate morphology and increased levels of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) and of androgen receptor and 5α-reductase expression. Moreover, testosterone injections induced a significant increase in markers of inflammation, apoptosis and oxidative stress. Our results show that um-PEA/Baic is capable of decreasing prostate weight and DHT production in BPH-induced rats, as well as being able to modulate apoptotic and inflammatory pathways and oxidative stress. These effects were most likely related to the synergy between the anti-inflammatory properties of um-PEA and the antioxidant effects of Baic. These results support the view that um-PEA/Baic should be further studied as a potent candidate for the management of BPH.
Keywords: androgen receptor; baicalein; benign prostatic hyperplasia; inflammation; oxidative stress; palmitoylethanolamide.
Conflict of interest statement
Salvatore Cuzzocrea is a coinventor on patent WO2013121449 A8 (Epitech Group Srl), which deals with methods and compositions for the modulation of amidases capable of hydrolyzing N-acylethanolamines employable in the treatment of inflammatory diseases. This invention is wholly unrelated to the present study. Moreover, Cuzzocrea is also, with the Epitech Group, a coinventor on the patents EP 2 821 083, MI2014 A001495 and 102015000067344, which are unrelated to this study. The remaining authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Fang T., Xue Z.S., Li J.X., Liu J.K., Wu D., Li M.Q., Song Y.T., Yun S.F., Yan J. Rauwolfia vomitoria extract suppresses benign prostatic hyperplasia by reducing expression of androgen receptor and 5alpha-reductase in a rat model. J. Integr. Med. 2020;19:258–264. doi: 10.1016/j.joim.2020.12.002. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Minutoli L., Rinaldi M., Marini H., Irrera N., Crea G., Lorenzini C., Puzzolo D., Valenti A., Pisani A., Adamo E.B., et al. Apoptotic Pathways Linked to Endocrine System as Potential Therapeutic Targets for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016;17:1311. doi: 10.3390/ijms17081311. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

