Clinical Practice of Photodynamic Therapy Using Talaporfin Sodium for Esophageal Cancer
- PMID: 34202917
- PMCID: PMC8268336
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10132785
Clinical Practice of Photodynamic Therapy Using Talaporfin Sodium for Esophageal Cancer
Abstract
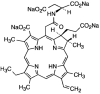
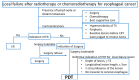
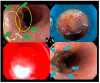
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) using a conventional photosensitizer was approved for esophageal cancer in the early 1990s; however, it was replaced by other conventional treatment modalities in clinical practice because of the high frequency of cutaneous phototoxicity and esophageal stricture after the procedure. The second-generation photosensitizer, talaporfin sodium, which features more rapid clearance from the body, was developed to reduce skin phototoxicity, and talaporfin sodium can be excited at longer-wavelength lights comparing with a conventional photosensitizer. Endoscopic PDT using talaporfin sodium was initially developed for the curative treatment of central-type early lung cancer in Japan, and was approved in the early 2000s. After preclinical experiments, PDT using talaporfin sodium was investigated for patients with local failure after chemoradiotherapy, which was the most serious unmet need in the practice of esophageal cancer. According to the favorable results of a multi-institutional clinical trial, PDT using talaporfin sodium was approved as an endoscopic salvage treatment for patients with local failure after chemoradiotherapy for esophageal cancer. While PDT using talaporfin sodium is gradually spreading in clinical practice, further evaluation at the point of clinical benefit is necessary to determine the importance of PDT in the treatment of esophageal cancer.
Keywords: esophageal cancer; photodynamic therapy; talaporfin sodium.
Conflict of interest statement
T.Y. received lecture fees from Meiji Seika Pharma. Other authors have no conflict of interest to be declared.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

