Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Mediated Regulation of Membrane Biochemistry and Tumor Cell Membrane Integrity
- PMID: 34203433
- PMCID: PMC8304949
- DOI: 10.3390/membranes11070479
Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Mediated Regulation of Membrane Biochemistry and Tumor Cell Membrane Integrity
Abstract
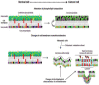
Particular dramatic macromolecule proteins are responsible for various cellular events in our body system. Lipids have recently recognized a lot more attention of scientists for understanding the relationship between lipid and cellular function and human health However, a biological membrane is formed with a lipid bilayer, which is called a P-L-P design. Our body system is balanced through various communicative signaling pathways derived from biological membrane proteins and lipids. In the case of any fatal disease such as cancer, the biological membrane compositions are altered. To repair the biological membrane composition and prevent cancer, dietary fatty acids, such as omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, are essential in human health but are not directly synthesized in our body system. In this review, we will discuss the alteration of the biological membrane composition in breast cancer. We will highlight the role of dietary fatty acids in altering cellular composition in the P-L-P bilayer. We will also address the importance of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids to regulate the membrane fluidity of cancer cells.
Keywords: ALA and GLA; P–L–P membrane channel; biological membrane; breast cancer; membrane remodeling; polyunsaturated fatty acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Hussein M.R., Hassan H.I. Analysis of the mononuclear inflammatory cell infiltrate in the normal breast, benign proliferative breast disease, in situ and infiltrating ductal breast carcinomas: Preliminary observations. J. Clin. Pathol. 2006;59:972–977. doi: 10.1136/jcp.2005.031252. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

