Development of a Macrophage-Based ADCC Assay
- PMID: 34204268
- PMCID: PMC8234572
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines9060660
Development of a Macrophage-Based ADCC Assay
Abstract
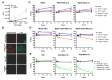
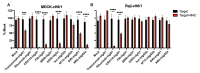
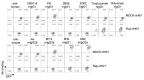
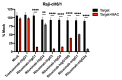
Fc-dependent effector functions are an important determinant of the in vivo potency of therapeutic antibodies. Effector function is determined by the combination of FcRs bound by the antibody and the cell expressing the relevant FcRs, leading to antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). A number of ADCC assays have been developed; however, they suffer from limitations in terms of throughput, reproducibility, and in vivo relevance. Existing assays measure NK cell-mediated ADCC activity; however, studies suggest that macrophages mediate the effector function of many antibodies in vivo. Here, we report the development of a macrophage-based ADCC assay that relies on luciferase expression in target cells as a measure of live cell number. In the presence of primary mouse macrophages and specific antibodies, loss of luciferase signal serves as a surrogate for ADCC-dependent killing. We show that the assay functions for a variety of mouse and human isotypes with a model antigen/antibody complex in agreement with the known effector function of the isotypes. We also use this assay to measure the activity of a number of influenza-specific antibodies and show that the assay correlates well with the known in vivo effector functions of these antibodies.
Keywords: ADCC; hemagglutinin; influenza; macrophage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Uchida J., Hamaguchi Y., Oliver J.A., Ravetch J.V., Poe J.C., Haas K.M., Tedder T.F. The innate mononuclear phagocyte network depletes B lymphocytes through fc receptor–dependent mechanisms during Anti-CD20 antibody immunotherapy. J. Exp. Med. 2004;199:1659–1669. doi: 10.1084/jem.20040119. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Grugan K.D., McCabe F.L., Kinder M., Greenplate A., Harman B.C., Ekert J.E., Van Rooijen N., Anderson G.M., Nemeth J.A., Strohl W.R., et al. Tumor-Associated Macrophages Promote Invasion while Retaining Fc-Dependent Anti-Tumor Function. J. Immunol. 2012;189:5457–5466. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1201889. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Beatty G.L., Chiorean E.G., Fishman M.P., Saboury B., Teitelbaum U.R., Sun W., Huhn R.D., Song W., Li D., Sharp L.L., et al. CD40 Agonists Alter Tumor Stroma and Show Efficacy against Pancreatic Carcinoma in Mice and Humans. Science. 2011;331:1612–1616. doi: 10.1126/science.1198443. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

