Risk Factors and Outcome of Multidrug-Resistant Infections after Heart Transplant: A Contemporary Single Center Experience
- PMID: 34205082
- PMCID: PMC8230299
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms9061210
Risk Factors and Outcome of Multidrug-Resistant Infections after Heart Transplant: A Contemporary Single Center Experience
Abstract
(1) Background: The aim of this study was to assess risk factors for multidrug-resistant/extensively drug-resistant (MDR/XDR) bacterial infections in heart transplant (HT) patients within three months after surgery and its impact on patient outcome. (2) Methods: Retrospective analysis of clinical, hemato-chemical, imaging, treatment and outcome data from 47 heart transplant recipients from January 2016 to December 2018. MDR/XDR infections were compared to non-MDR/XDR and noninfected patients. (3) Results: Most participants were males, median age 51 years: 35 (74.5%) developed an infection after HT; 14 (29.8%) were MDR/XDR infections. Prolonged hospital stay before HT correlated to MDR/XDR infection (p < 0.001). Sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA) score at sampling day was higher in MDR/XDR (p = 0.027). MDR/XDR were mostly blood-stream (BSI) (p = 0.043) and skin-soft tissue (SSTI) (p = 0.047) infections. Gram-negative infections were the most frequent, specifically carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antibiotic therapy duration for MDR/XDR infections was longer (p = 0.057), eradication rate lower (p = 0.083) and hospital stay longer (p = 0.005) but not associated with a worse outcome. (4) Conclusions: MDR/XDR infections affect compromised HT recipients with a history of prolonged hospitalization, causing a lower rate of eradication and increased hospital stay. These frequently present as BSI and SSTI. We emphasize the need to prevent contamination of central venous catheters and the surgical site.
Keywords: MDR; XDR; heart transplant; hospitalization; infection; outcome; risk factors.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors have no conflict of interest to disclose relevant to the content of this study. EDM received grant support and personal fees, outside of this work, from Roche, Pfizer, MSD, Angelini, Bio-Merieux, Abbvie, Nordic Pharma, Sanofi-Aventis, Medtronic, and DiaSorin. RoZ and RA received personal fees, outside of this work, from Nordic Pharma.
Figures
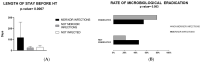

References
-
- Mehra M., Canter C.E., Hannan M.M., Semigran M.J., Uber P.A., Baran D.A., Danziger-Isakov L., Kirklin J.K., Kirk R., Kushwaha S.S., et al. The 2016 International Society for Heart Lung Transplantation listing criteria for heart transplantation: A 10-year update. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2016;35:1–23. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2015.10.023. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chambers D.C., Cherikh W.S., Harhay M.O., Hayes D., Hsich E., Khush K.K., Meiser B., Potena L., Rossano J.W., Toll A.E., et al. The International Thoracic Organ Transplant Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: Thirty-sixth adult lung and heart–lung transplantation Report—2019; Focus theme: Donor and recipient size match. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2019;38:1042–1055. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2019.08.001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

