High Rates of Hidden HCV Infections among Hospitalized Patients Aged 55-85
- PMID: 34205096
- PMCID: PMC8227146
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens10060695
High Rates of Hidden HCV Infections among Hospitalized Patients Aged 55-85
Abstract
Background and aims: The WHO has solicited all countries to eliminate HCV by 2030. The Italian government started routine screening for HCV infection in January 2021, initially targeting subjects born between 1969 and 1989. With the aim of achieving micro-elimination, we designed a hospital-wide project focusing on inpatients born from 1935 to 1985 and conducted it in our institution.
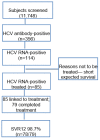
Method: All inpatients aged 35 to 85, admitted from 10 February 2020 to 9 February 2021 for many different diseases and conditions underwent HCV antibody (HCVAb) testing by third-generation ELISA. When positive, reflex HCV RNA testing and genotyping were performed. Clinical history, fibrosis diagnosis, laboratory data and concomitant medications were available for all.
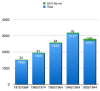
Results: The HCV screening rate of inpatients was 100%. In total, 11,748 participants were enrolled, of whom 53.50% were male. The HCVAb positivity rate was 3.03%. The HCVAb rate increased with age and was higher for patients born between 1935 and 1944 (4.81%). The rate of HCV RNA positivity was 0.97%. The vast majority (80.70%) of HCV RNA-positive participants were 55 or older; in about 40% of cases, HCV RNA-positive patients were unaware of their infection. Although 16 patients died after HCV chronic infection diagnosis (two due COVID-19) or HCV treatment prescription (one due to COVID-19), 74.56% of patient HCV diagnoses were linked to HCV treatment, despite their co-morbidities. All patients older than 65 who died had an active HCV infection.
Conclusion: The present study revealed a rate of active HCV infections among inpatients lower than what has been reported in the past in the general population; this appears to be a result of the widespread use of pangenotypic direct-acting antiviral agents (DAAs). The overall rate of active infection was lower than the rate observed in the 1935-1954 cohort. The high rate of inpatients unaware of HCV infections and the high number of deaths among subjects with an active HCV infection born from 1935 to 1954, suggest that, at least in southern Italy, targeted screening of this birth cohort may be required to reduce the number of undiagnosed cases and hidden infections.
Keywords: HCV; birth cohort; linkage-to-care; micro-elimination; screening; sofosbuvir/velpatasvir.
Conflict of interest statement
Alessandra Mangia serves as consultant for Angelini, Gilead Science, Intercept, MSD. All the other Authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization Global Health Sector Strategy on Viral Hepatitis 2016–2021. [(accessed on 2 January 2021)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/hepatitis/strategy2016-2021/ghss-hep/en/
-
- Razavi H., Robbins S., Zeuzem S., Negro F., Buti M., Duberg A.S., Roudot-Thoraval F., Craxi A., Manns M., Marinho R.T., et al. Hepatitis C virus prevalence and level of intervention required to achieve the WHO targets for elimination in the European Union by 2030: A modelling study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017;2:325–336. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(17)30045-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Andriulli A., Stroffolini T., Mariano A., Valvano M.R., Grattagliano I., Ippolito A.M., Grossi A., Brancaccio G., Coco C., Russello M., et al. Declining prevalence and increasing awareness of HCV infection in Italy: A population-based survey in five metropolitan areas. Eur. Intern. Med. 2018;53:79–84. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2018.02.015. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lazarus J.V., Safreed-Harmon K., Thursz M.R., Dillon J.F., El-Sayed M.H., Elsharkawy A.M., Hatzakis A., Jadoul M., Prestileo T., Razavi H., et al. The micro-elimination approach to eliminating hepatitis C: Strategic and operational considerations. Semin. Liver Dis. 2018;38:181–192. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1666841. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous