Clinical Performance of Paraoxonase-1-Related Variables and Novel Markers of Inflammation in Coronavirus Disease-19. A Machine Learning Approach
- PMID: 34205807
- PMCID: PMC8234277
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox10060991
Clinical Performance of Paraoxonase-1-Related Variables and Novel Markers of Inflammation in Coronavirus Disease-19. A Machine Learning Approach
Abstract
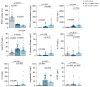
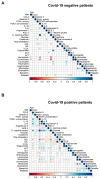
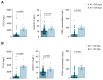
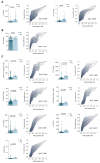
SARS-CoV-2 infection produces a response of the innate immune system causing oxidative stress and a strong inflammatory reaction termed 'cytokine storm' that is one of the leading causes of death. Paraoxonase-1 (PON1) protects against oxidative stress by hydrolyzing lipoperoxides. Alterations in PON1 activity have been associated with pro-inflammatory mediators such as the chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 (CCL2), and the glycoprotein galectin-3. We aimed to investigate the alterations in the circulating levels of PON1, CCL2, and galectin-3 in 126 patients with COVID-19 and their interactions with clinical variables and analytical parameters. A machine learning approach was used to identify predictive markers of the disease. For comparisons, we recruited 45 COVID-19 negative patients and 50 healthy individuals. Our approach identified a synergy between oxidative stress, inflammation, and fibrogenesis in positive patients that is not observed in negative patients. PON1 activity was the parameter with the greatest power to discriminate between patients who were either positive or negative for COVID-19, while their levels of CCL2 and galectin-3 were similar. We suggest that the measurement of serum PON1 activity may be a useful marker for the diagnosis of COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; biomarkers; chemokines; galectin-3; machine learning; paraoxonase-1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funder had no role in the study design, data collection, analysis, decision to publish, or manuscript preparation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Influence of Surgical Procedures on Serum Paraoxonase-1-Related Variables and Markers of Inflammation in Hospitalized Patients.J Invest Surg. 2021 Feb;34(2):216-224. doi: 10.1080/08941939.2019.1597223. Epub 2019 Apr 4. J Invest Surg. 2021. PMID: 30947571
-
Preliminary study on serum paraoxonase-1 status and chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 in hospitalized elderly patients with catheter-associated asymptomatic bacteriuria.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2016 Sep;35(9):1417-24. doi: 10.1007/s10096-016-2679-8. Epub 2016 Jun 22. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27334497
-
Disruption of CCR5 signaling to treat COVID-19-associated cytokine storm: Case series of four critically ill patients treated with leronlimab.J Transl Autoimmun. 2021;4:100083. doi: 10.1016/j.jtauto.2021.100083. Epub 2021 Jan 6. J Transl Autoimmun. 2021. PMID: 33521616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A preliminary study of paraoxonase-1 in infected patients with an indwelling central venous catheter.Clin Biochem. 2016 Apr;49(6):449-457. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2015.11.006. Epub 2015 Nov 11. Clin Biochem. 2016. PMID: 26562028
-
COVID-19, Mast Cells, Cytokine Storm, Psychological Stress, and Neuroinflammation.Neuroscientist. 2020 Oct-Dec;26(5-6):402-414. doi: 10.1177/1073858420941476. Epub 2020 Jul 18. Neuroscientist. 2020. PMID: 32684080 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Low-Dose Radiotherapy on the Circulating Levels of Paraoxonase-1-Related Variables and Markers of Inflammation in Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jun 16;11(6):1184. doi: 10.3390/antiox11061184. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35740079 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning and semi-targeted lipidomics identify distinct serum lipid signatures in hospitalized COVID-19-positive and COVID-19-negative patients.Metabolism. 2022 Jun;131:155197. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2022.155197. Epub 2022 Apr 2. Metabolism. 2022. PMID: 35381232 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Reprogramming in Respiratory Viral Infections: A Focus on SARS-CoV-2, Influenza, and Respiratory Syncytial Virus.Biomolecules. 2025 Jul 16;15(7):1027. doi: 10.3390/biom15071027. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40723899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Like a Rolling Stone? A Review on Spontaneous Clearance of Hepatitis C Virus Infection.Viruses. 2024 Aug 30;16(9):1386. doi: 10.3390/v16091386. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39339862 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Paraoxonase 1 rs662 polymorphism, its related variables, and COVID-19 intensity: Considering gender and post-COVID complications.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2023 Dec;248(23):2351-2362. doi: 10.1177/15353702221128563. Epub 2022 Oct 31. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2023. PMID: 36314852 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

