Synthesis and Neurotropic Activity of New Heterocyclic Systems: Pyridofuro[3,2- d]pyrrolo[1,2- a]pyrimidines, Pyridofuro[3,2- d]pyrido[1,2- a]pyrimidines and Pyridofuro[3',2':4,5]pyrimido[1,2- a]azepines
- PMID: 34205930
- PMCID: PMC8198642
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26113320
Synthesis and Neurotropic Activity of New Heterocyclic Systems: Pyridofuro[3,2- d]pyrrolo[1,2- a]pyrimidines, Pyridofuro[3,2- d]pyrido[1,2- a]pyrimidines and Pyridofuro[3',2':4,5]pyrimido[1,2- a]azepines
Abstract
Background: Neurotic disturbances, anxiety, neurosis-like disorders, and stress situations are widespread. Benzodiazepine tranquillizers have been found to be among the most effective antianxiety drugs. The pharmacological action of benzodiazepines is due to their interaction with the supra-molecular membrane GABA-a-benzodiazepine receptor complex, linked to the Cl-ionophore. Benzodiazepines enhance GABA-ergic transmission and this has led to a study of the role of GABA in anxiety. The search for anxiolytics and anticonvulsive agents has involved glutamate-ergic, 5HT-ergic substances and neuropeptides. However, each of these well-known anxiolytics, anticonvulsants and cognition enhancers (nootropics) has repeatedly been reported to have many adverse side effects, therefore there is an urgent need to search for new drugs able to restore damaged cognitive functions without causing significant adverse reactions.
Objective: Considering the relevance of epilepsy diffusion in the world, we have addressed our attention to the discovery of new drugs in this field Thus our aim is the synthesis and study of new compounds with antiepileptic (anticonvulsant) and not only, activity.
Methods: For the synthesis of compounds classical organic methods were used and developed. For the evaluation of biological activity some anticonvulsant and psychotropic methods were used.
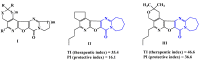
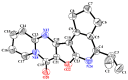
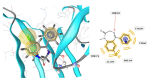
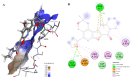
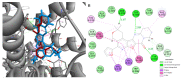
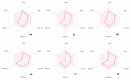
Results: As a result of multistep reactions 26 new, five-membered heterocyclic systems were obtained. PASS prediction of anticonvulsant activity was performed for the whole set of the designed molecules and probability to be active Pa values were ranging from 0.275 to 0.43. The studied compounds exhibit protection against pentylenetetrazole (PTZ) seizures, anti-thiosemicarbazides effect as well as some psychotropic effect. The biological assays evidenced that some of the studied compounds showed a high anticonvulsant activity by antagonism with pentylenetetrazole. The toxicity of compounds is low and they do not induce muscle relaxation in the studied doses. According to the study of psychotropic activity it was found that the selected compounds have an activating behavior and anxiolytic effects on the models of "open field" and "elevated plus maze" (EPM). The data obtained indicate the anxiolytic (anti-anxiety) activity of the derivatives of pyrimidines, especially pronounced in compounds 6n, 6b, and 7c. The studied compounds increase the latent time of first immobilization on the model of "forced swimming" (FST) and exhibit some antidepressant effect similarly to diazepam. Docking studies revealed that compound 6k bound tightly in the active site of GABAA receptor with a value of the scoring function that estimates free energy of binding (ΔG) at -7.95 kcal/mol, while compound 6n showed the best docking score and seems to be dual inhibitor of SERT transporter as well as 5-HT1A receptor.
Conclusions: Тhe selected compounds have an anticonvulsant, activating behavior and anxiolytic effects, at the same time exhibit some antidepressant effect.
Keywords: anticonvulsant action; furo[3,2-d]pyrido[1,2-a]pyrimidines; furo[3,2-d]pyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrimidines; furo[3′,2′:4,5] pyrimido [1,2-a]azepines; neurotropic activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Mkrtchyan A.P., Kazaryan S.G., Noravyan A.S., Dzhagatspanyan I.A., Nazaryan I.M., Akopyan A.G. Synthesis and anticonvulsive activity of a series of new pyrano(thiopyrano,pyrido)[4′,3′:4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidines. Pharm. Chem. J. 1998;32:469–473. doi: 10.1007/BF02539219. - DOI
-
- Kapustina M.V., Amelkin O.Y., Kharizomenova A.I., Shvedov V.I., Filitis L.N. Synthesis and antitubercular activity of benzothieno[2,3-d]pyrimidines. Pharm. Chem. J. 1991;25:475–477. doi: 10.1007/BF00772002. - DOI
-
- Ferrara M., Crescenzi B., Donghi M., Muraglia E., Nizi E., Pesci S., Summa V., Gardelli C. Synthesis of a hexahydropyrimido[1,2-a]azepine-2-carboxamide derivative useful as an HIV integrase inhibitor. Tetrahedron Lett. 2007;48:8379–8382. doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2007.09.072. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

