Multifaced Roles of HDL in Sepsis and SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Renal Implications
- PMID: 34205975
- PMCID: PMC8197836
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22115980
Multifaced Roles of HDL in Sepsis and SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Renal Implications
Abstract
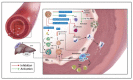
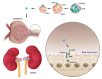
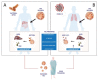
High-density lipoproteins (HDLs) are a class of blood particles, principally involved in mediating reverse cholesterol transport from peripheral tissue to liver. Omics approaches have identified crucial mediators in the HDL proteomic and lipidomic profile, which are involved in distinct pleiotropic functions. Besides their role as cholesterol transporter, HDLs display anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic, anti-thrombotic, and anti-infection properties. Experimental and clinical studies have unveiled significant changes in both HDL serum amount and composition that lead to dysregulated host immune response and endothelial dysfunction in the course of sepsis. Most SARS-Coronavirus-2-infected patients admitted to the intensive care unit showed common features of sepsis disease, such as the overwhelmed systemic inflammatory response and the alterations in serum lipid profile. Despite relevant advances, episodes of mild to moderate acute kidney injury (AKI), occurring during systemic inflammatory diseases, are associated with long-term complications, and high risk of mortality. The multi-faceted relationship of kidney dysfunction with dyslipidemia and inflammation encourages to deepen the clarification of the mechanisms connecting these elements. This review analyzes the multifaced roles of HDL in inflammatory diseases, the renal involvement in lipid metabolism, and the novel potential HDL-based therapies.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2 infection; acute kidney injury (AKI); dysfunctional HDL; lipid profile changes; sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
High-density lipoproteins and COVID-19: preparing the next pandemic.J Lipid Res. 2025 May;66(5):100779. doi: 10.1016/j.jlr.2025.100779. Epub 2025 Mar 14. J Lipid Res. 2025. PMID: 40090619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Good Cholesterol Gone Bad? HDL and COVID-19.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 22;22(19):10182. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910182. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638523 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-density lipoproteins during sepsis: from bench to bedside.Crit Care. 2020 Apr 7;24(1):134. doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-02860-3. Crit Care. 2020. PMID: 32264946 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HDL-scavenger receptor B type 1 facilitates SARS-CoV-2 entry.Nat Metab. 2020 Dec;2(12):1391-1400. doi: 10.1038/s42255-020-00324-0. Epub 2020 Nov 26. Nat Metab. 2020. PMID: 33244168
-
HDL and SARS CoV-2: emerging theragnostic implications.Trends Mol Med. 2024 May;30(5):425-428. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2024.02.001. Epub 2024 Mar 1. Trends Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38431503 Review.
Cited by
-
Persistence of Lipoproteins and Cholesterol Alterations after Sepsis: Implication for Atherosclerosis Progression.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 29;22(19):10517. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910517. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638860 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 vulnerabilities are intensified by declining human serum albumin levels.Exp Physiol. 2022 Jul;107(7):674-682. doi: 10.1113/EP089703. Epub 2021 Aug 13. Exp Physiol. 2022. PMID: 34275164 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 and lipids. The role of lipid disorders and statin use in the prognosis of patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection.Lipids Health Dis. 2021 Oct 25;20(1):141. doi: 10.1186/s12944-021-01563-0. Lipids Health Dis. 2021. PMID: 34689776 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Shared genetic correlations between kidney diseases and sepsis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jul 17;15:1396041. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1396041. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39086896 Free PMC article.
-
Cholesterol and Cholesterol-Lowering Medications in COVID-19-An Unresolved Matter.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 29;25(19):10489. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910489. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408818 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

