Characterization of Phase I Hepatic Metabolites of Anti-Premature Ejaculation Drug Dapoxetine by UHPLC-ESI-Q-TOF
- PMID: 34206424
- PMCID: PMC8270242
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26133794
Characterization of Phase I Hepatic Metabolites of Anti-Premature Ejaculation Drug Dapoxetine by UHPLC-ESI-Q-TOF
Abstract
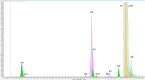
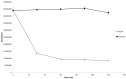
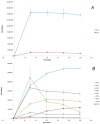
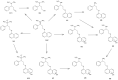
Determination of the metabolism pathway of xenobiotics undergoing the hepatic pass is a crucial aspect in drug development since the presence of toxic biotransformation products may result in significant side effects during the therapy. In this study, the complete hepatic metabolism pathway of dapoxetine established according to the human liver microsome assay with the use of a high-resolution LC-MS system was described. Eleven biotransformation products of dapoxetine, including eight metabolites not reported in the literature so far, were detected and identified. N-dealkylation, hydroxylation, N-oxidation and dearylation were found to be the main metabolic reactions for the investigated xenobiotic. In silico analysis of toxicity revealed that the reaction of didesmethylation may contribute to the increased carcinogenic potential of dapoxetine metabolites. On the other hand, N-oxidation and aromatic hydroxylation biotransformation reactions possibly lead to the formation of mutagenic compounds.
Keywords: HLM; biotransformation; chromatography; in silico toxicity; mass spectrometry; metabolites.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Danielson P.B. The Cytochrome P450 Superfamily: Biochemistry, Evolution and Drug Metabolism in Humans. [(accessed on 19 January 2020)]; Available online: http://www.eurekaselect.com/64118/article. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

