Molecular Mechanisms during Hepatitis B Infection and the Effects of the Virus Variability
- PMID: 34207116
- PMCID: PMC8235420
- DOI: 10.3390/v13061167
Molecular Mechanisms during Hepatitis B Infection and the Effects of the Virus Variability
Abstract
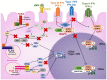
The immunopathogenesis and molecular mechanisms involved during a hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection have made the approaches for research complex, especially concerning the patients' responses in the course of the early acute stage. The study of molecular bases involved in the viral clearance or persistence of the infection is complicated due to the difficulty to detect patients at the most adequate points of the disease, especially in the time lapse between the onset of the infection and the viral emergence. Despite this, there is valuable data obtained from animal and in vitro models, which have helped to clarify some aspects of the early immune response against HBV infection. The diversity of the HBV (genotypes and variants) has been proven to be associated not only with the development and outcome of the disease but also with the response to treatments. That is why factors involved in the virus evolution need to be considered while studying hepatitis B infection. This review brings together some of the published data to try to explain the immunological and molecular mechanisms involved in the different stages of the infection, clinical outcomes, viral persistence, and the impact of the variants of HBV in these processes.
Keywords: HBV interference; HBV sensing; HBV variability; acute hepatitis B; acute liver failure; chronic hepatitis B; immune pathogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Coexistence of hepatitis B virus quasispecies enhances viral replication and the ability to induce host antibody and cellular immune responses.J Virol. 2014 Aug;88(15):8656-66. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01123-14. Epub 2014 May 21. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24850745 Free PMC article.
-
Immunopathogenesis of HBV Infection.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1179:71-107. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-9151-4_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 31741334 Review.
-
Hepatitis B virus genotypes and hepatitis B surface antigen mutations in family contacts of hepatitis B virus infected patients with occult hepatitis B virus infection.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009 Apr;24(4):588-98. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2008.05727.x. Epub 2009 Jan 13. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009. PMID: 19207682
-
Does hepatitis B virus (HBV) genotype influence the clinical outcome of HBV infection?J Viral Hepat. 1999 Jul;6(4):299-304. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2893.1999.00174.x. J Viral Hepat. 1999. PMID: 10607244
-
HBV evolution and genetic variability: Impact on prevention, treatment and development of antivirals.Antiviral Res. 2021 Feb;186:104973. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104973. Epub 2020 Nov 6. Antiviral Res. 2021. PMID: 33166575 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms of Ganweikang Tablets against Chronic Hepatitis B: A Comprehensive Study of Network Analysis, Molecular Docking, and Chemical Profiling.Biomed Res Int. 2023 May 8;2023:8782892. doi: 10.1155/2023/8782892. eCollection 2023. Biomed Res Int. 2023. PMID: 37197593 Free PMC article.
-
NLRP3 Inflammasome in Acute and Chronic Liver Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 20;25(8):4537. doi: 10.3390/ijms25084537. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38674122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Special Issue "Structural Variations and Molecular Genetics of Hepatitis Virus and Related Viruses".Viruses. 2021 Jul 27;13(8):1456. doi: 10.3390/v13081456. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34452322 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B in Pediatric Population: Observational Retrospective Study in Romania.Life (Basel). 2024 Mar 7;14(3):348. doi: 10.3390/life14030348. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38541675 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into induction of the immune response by the hepatitis B vaccine.World J Gastroenterol. 2022 Aug 21;28(31):4249-4262. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i31.4249. World J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36159002 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pastor F., Herrscher C., Patient R., Eymieux S., Moreau A., Burlaud-Gaillard J., Seigneuret F., De Rocquigny H., Roingeard P., Hourioux C. Direct interaction between the hepatitis B virus core and envelope proteins analyzed in a cellular context. Sci. Rep. 2019;9:1–12. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-52824-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

