Molecular Mechanisms during Hepatitis B Infection and the Effects of the Virus Variability
- PMID: 34207116
- PMCID: PMC8235420
- DOI: 10.3390/v13061167
Molecular Mechanisms during Hepatitis B Infection and the Effects of the Virus Variability
Abstract
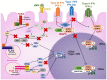
The immunopathogenesis and molecular mechanisms involved during a hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection have made the approaches for research complex, especially concerning the patients' responses in the course of the early acute stage. The study of molecular bases involved in the viral clearance or persistence of the infection is complicated due to the difficulty to detect patients at the most adequate points of the disease, especially in the time lapse between the onset of the infection and the viral emergence. Despite this, there is valuable data obtained from animal and in vitro models, which have helped to clarify some aspects of the early immune response against HBV infection. The diversity of the HBV (genotypes and variants) has been proven to be associated not only with the development and outcome of the disease but also with the response to treatments. That is why factors involved in the virus evolution need to be considered while studying hepatitis B infection. This review brings together some of the published data to try to explain the immunological and molecular mechanisms involved in the different stages of the infection, clinical outcomes, viral persistence, and the impact of the variants of HBV in these processes.
Keywords: HBV interference; HBV sensing; HBV variability; acute hepatitis B; acute liver failure; chronic hepatitis B; immune pathogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Pastor F., Herrscher C., Patient R., Eymieux S., Moreau A., Burlaud-Gaillard J., Seigneuret F., De Rocquigny H., Roingeard P., Hourioux C. Direct interaction between the hepatitis B virus core and envelope proteins analyzed in a cellular context. Sci. Rep. 2019;9:1–12. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-52824-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

