MUC1: Structure, Function, and Clinic Application in Epithelial Cancers
- PMID: 34207342
- PMCID: PMC8234110
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22126567
MUC1: Structure, Function, and Clinic Application in Epithelial Cancers
Abstract
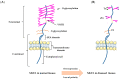
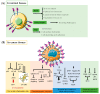
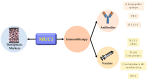
The transmembrane glycoprotein mucin 1 (MUC1) is a mucin family member that has different functions in normal and cancer cells. Owing to its structural and biochemical properties, MUC1 can act as a lubricant, moisturizer, and physical barrier in normal cells. However, in cancer cells, MUC1 often undergoes aberrant glycosylation and overexpression. It is involved in cancer invasion, metastasis, angiogenesis, and apoptosis by virtue of its participation in intracellular signaling processes and the regulation of related biomolecules. This review introduces the biological structure and different roles of MUC1 in normal and cancer cells and the regulatory mechanisms governing these roles. It also evaluates current research progress and the clinical applications of MUC1 in cancer therapy based on its characteristics.
Keywords: MUC1; MUC1 cell barrier; epithelial cancer; immunotherapy; therapeutic biomarkers; tumor oncogene.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

